Figure 6. Secretagogin regulates CRH release in vitro and in vivo.
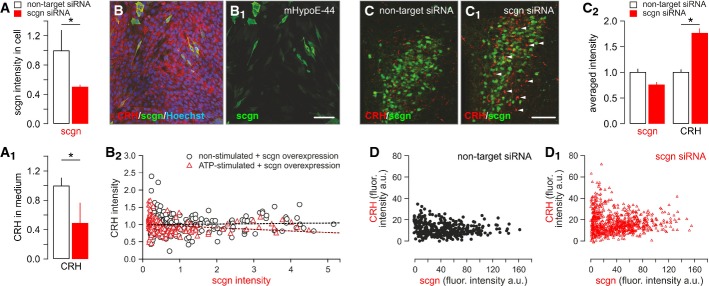
- A, A1 siRNA-mediated secretagogin (scgn) knockdown in cultured hypothalamic neurons, as indicated by reduced secretagogin immunoreactivity (A) and decreased CRH content in the culture medium (A1).
- B–B2 Transient overexpression of secretagogin in immortalized CRH-expressing mHypoE-N44 hypothalamic cells significantly reduced CRH immunofluorescence intensity in secretagogin+ cell bodies, indirectly supporting enhanced CRH release. All experiments were performed in triplicate. Scale bar: 50 nm.
- C, C1 siRNA-mediated in vivo silencing of secretagogin mRNA expression in the PVN provoked somatic CRH accumulation (arrowheads). Scale bar: 150 μm.
- C2 Quantitative analysis demonstrating significantly increased somatic CRH contents. Note that somatic secretagogin levels remained unchanged, which we interpret as data on a neuronal contingent not affected by siRNA silencing. The lack of secretagogin/CRH co-localization suggests that secretagogin expression fell below detection threshold in many CRH+ neurons.
- D, D1 Individual data points show maximal CRH fluorescence intensity (gray scale arbitrary unit (a.u.) expression) in PVN neurons that have low or no secretagogin expression after siRNA infusion.
Data information: Data in (C2) were normalized to those in non-targeting siRNA controls. *P < 0.05 versus control.
