Figure 2. PRK5 is an atypical, enzymatically inactive RLK.
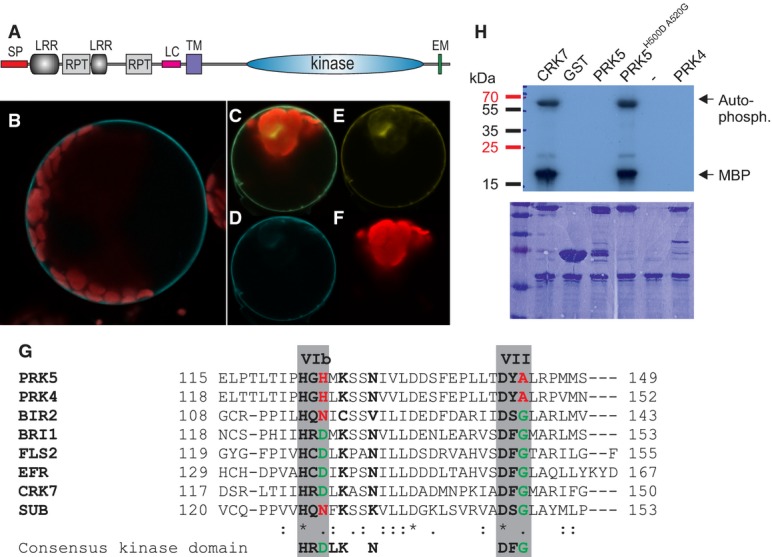
- A PRK5 domain structure: SP signal peptide (aa 1–39), LRR leucine-rich repeat, RPT internal repeat, LC region of low complexity, TM transmembrane domain (aa 282–304), EM Y-based sorting/endocytosis motif (YSSM; aa 670–673).
- B PRK5-CFP localized to the cell periphery in Col-0 mesophyll protoplasts.
- C–F Co-localization of PRK5-CFP and PM localized CAAX-YFP in Col-0 mesophyll protoplasts. (C) overlay; (D) PRK5-CFP (465–510 nm); (E) CAAX-YFP (521–587 nm); (F) chloroplast (636–711 nm).
- G Alignment of subdomains VIb and VII of the catalytic core of the kinase domains of active (BRI1, FLS2, EFR, CRK7) and inactive RLKs (PRK4, PRK5, BIR2, SUB). Residues marked in green highlight conservation of the consensus of active protein kinases while residues highlighted in red indicate deviations from the consensus sequence. An alignment of the full kinase domains for the RLKs used in this figure can be found in Supplementary Fig S11A.
- H Kinase activity of PRK5 in in vitro phosphorylation assays using γ32P-ATP and myelin-basic protein (MBP) as a substrate in the presence of 10 mM MnCl2. GST-PRK5 and GST-PRK4 did not show kinase activity. Mutation of conserved residues in kinase subdomains VIb and VII to reconstitute the consensus kinase domain motif restored GST-PRK5H500DA520G kinase activity. GST-CRK7 was used as a positive control. Upper panel shows autoradiograph, and lower panel shows the Coomassie-stained 15% SDS–polyacrylamide gel.
Data information: Experiments in (B–F and H) were repeated three times with similar results. Source data are available online for this figure.
