Figure 3. Rap1 pre-mRNA splicing and protein stability are impaired in cay1Δ cells.
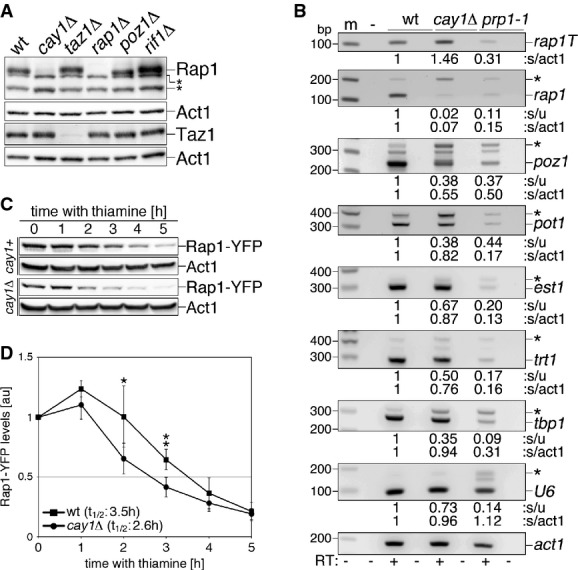
- A Western blot analysis of endogenous Rap1 and Taz1 in the indicated strains. Act1 was used as a loading control. Asterisks indicate cross-reacting bands.
- B RT–PCR analysis of splicing efficiencies of the indicated pre-mRNAs in wt and cay1Δ cells. The prp1-1 strain carries a thermosensitive allele of the splicing factor Prp1 and was used as a positive control for splicing impairment. prp1-1 cells were grown at 36°C for 4 h before harvesting. Amplification products corresponding to unspliced and spliced mRNAs are indicated by asterisks and gene names, respectively. rap1T indicates amplification products obtained with oligonucleotides spanning rap1+ exon 3 and thereby amplifying both spliced and unspliced mRNA. Intronless act1+ was used as a loading control. Numbers at the bottom of each panel are ratios between spliced and unspliced forms (s/u) and spliced and act1+ (s/act1). Values are expressed as fold increase over wt.
- C Western blot analysis of Rap1-YFP protein levels in the indicated strains upon nmt1 promoter shutoff by thiamine addition. Membranes were probed with antibodies against GFP and Act1 (loading control).
- D Quantification of Rap1-YFP protein levels in experiments as in (C). Rap1-YFP levels are expressed as fold increase over time 0 after normalization through Act1. Data points and error bars are averages and s.d. from at least four independent experiments. Statistical significance was assayed using the unpaired, two-tailed Student's t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 for cay1+ versus cay1Δ samples.
