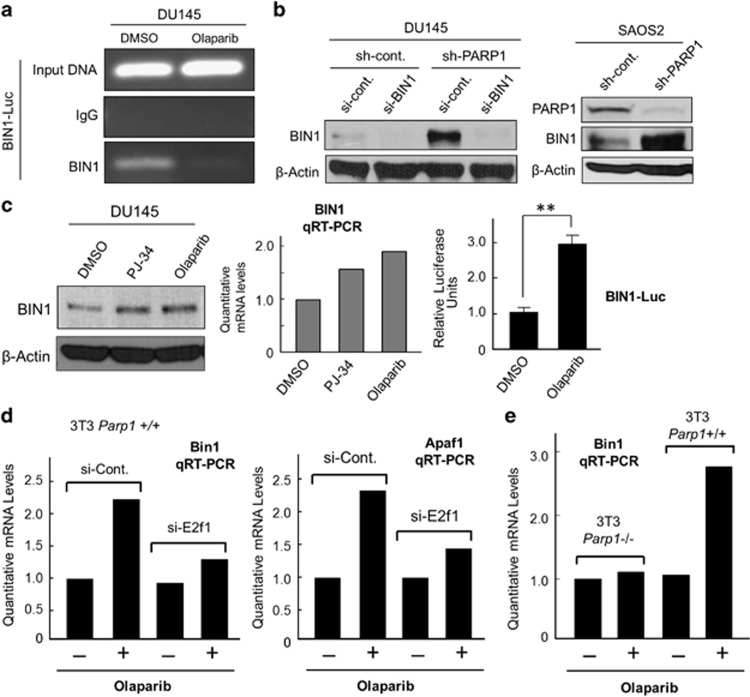
Figure 6.
PARP1 attenuation abolishes the E2F1 negative-feedback loop and robustly increases BIN1 levels. (a) Endogenous BIN1 levels on the BIN1–Luc promoter were analyzed by chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays in DU145 cells pretreated with DMSO or olaparib (10 μM, 72 h). (b, c) PARP1 depletion by sh-PARP1 or PARP1 inhibition by PJ-34 (10 μM, 72 h) or olaparib (10 μM, 72 h) was sufficient to increase BIN1 proteins, BIN1 transcripts, and BIN1 promoter activity in human cancer cells. **P<0.005. (d) qRT-PCR analyses of Bin1 and Apaf1 mRNA expression in mouse 3T3 Parp1+/+ fibroblasts transiently transfected with E2f1 si-RNA (si-E2f1), followed by the treatments with (+) or without (–) olaparib (10 μM, 72 h). As the negative control, scrambled si-control RNAs (si-Cont.) were used. (e) qRT-PCR analysis of Bin1 mRNA expression in mouse 3T3 Parp1+/+ and Parp1–/– cells treated with (+) or without (−) olaparib (10 μM, 72 h)