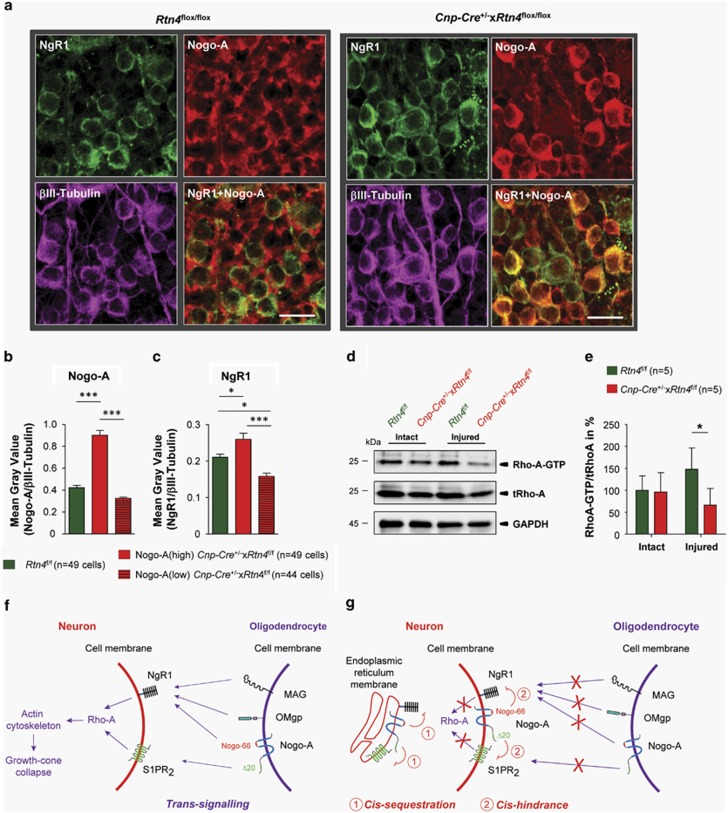
Figure 6.
The correlation of Nogo-A and NgR1 expression levels in RGCs suggests a possible cis-interaction. (a) NgR1, Nogo-A and βIII-Tubulin were examined by immunohistochemistry on retinal flat-mounts in Rtn4flox/flox and Cnp-Cre+/−xRtn4flox/flox KO mice. (b) Nogo-A-positive RGCs in the Cnp-Cre+/−xRtn4flox/flox mice were divided into high-(above the mean level of the control mice) and low-expressing cells. (c) The levels of NgR1 correlated with the Nogo-A levels in these two populations of intact RGCs. (d, e) Rho-A pull-down experiments revealed lower-activated Rho-A-GTP levels in the injured retinae of the Cnp-Cre+/−xRtn4flox/flox KO mice. (f) Cartoon showing trans-activation of the NgR1-S1PR2/Rho-A signaling pathway by oligodendroglial Nogo-A. (g) Hypothetical cis-interaction between Nogo-A and its receptors in neurons, on the intracellular side, in the endoplasmic reticulum or at the cell membrane, leading to the downstream signaling blockade of Rho-A. Scale bar: (a)=20 μm