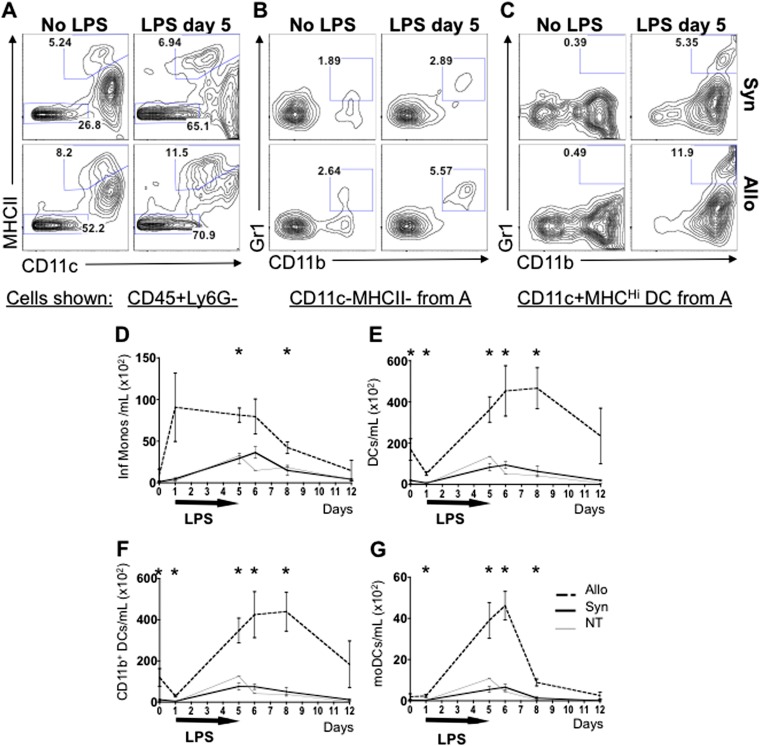
Figure 2.
Allogeneically transplanted mice exposed to inhaled LPS have increased pulmonary inflammatory monocytes and dendritic cells (DCs) compared with syngeneic or nontransplanted mice. Mice underwent an allogeneic HCT (Allo), syngeneic HCT (Syn), or no HCT (nontransplanted or NT) with subsequent daily exposures to aerosolized LPS for 5 days. Mice were killed without LPS exposure, at 4 hours after one LPS exposure, and at 4 hours, 24 hours, 72 hours, and 7 days after five daily LPS exposures. (A–C) Representative BAL cell flow cytometry plots are shown for Allo and Syn mice without LPS and 4 hours after five daily LPS exposures. (A) CD45+Ly6G− nonneutrophil leukocytes are shown. The highest percentage of CD11c+MHCIIHigh DCs is found in the Allo LPS-exposed mice as compared with Allo LPS-unexposed and Syn mice. (B) Among CD11c−MHCII− cells, the CD11b+ monocytes have the highest expression of Gr1 in the Allo LPS-exposed group. (C) When evaluating the Gr1 and CD11b expression on the DC population, the Allo LPS-exposed mice have the highest percentage of CD11b+ and of Gr1+CD11b+ double-positive DCs. (D–G) Total numbers of BAL monocyte and DC subsets are graphed. Allo mice exposed to LPS have higher absolute numbers of inflammatory Gr1+CD11b+ monocytes (D), DCs (E), total CD11b+ DC (F), and Gr1+CD11b+ monocyte-derived DCs (moDCs) (G) as compared with Syn and NT controls. Data represent the average ± SEM. *P < 0.05. Data have been replicated in two independent experiments.