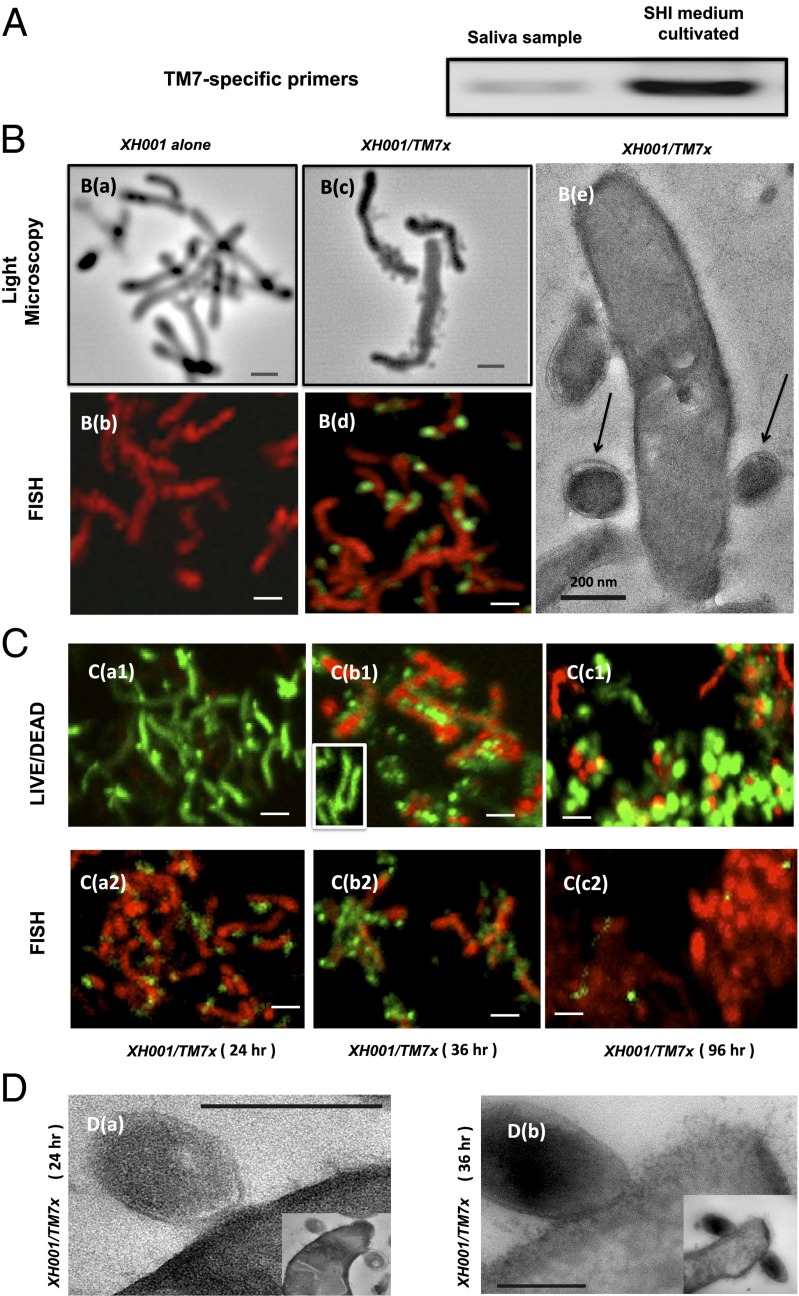
Fig. 1.
Cultivation and coisolation of TM7x with its host species Actinomyces spp. XH001. (A) PCR using a phylum-specific primer reveals the presence of TM7 within SHI medium-cultivated saliva samples. (B) Light microscopy and FISH images of XH100 monoculture (a and b) and XH100/TM7 coculture (c and d). (B, c) Cells of XH100 with several cells of TM7x attached to them. (B, d) Confocal laser scanning micrograph after hybridization with the cyanine5-labeled TM7567 (TM7x) and hexachloro-fluorescein–labeled universal eubacterial probe EUB338. XH001 appears red, whereas TM7 appears green. (B, e) TEM image of TM7x cell (indicated by arrows) attached to an XH001 cell. (Scale bars: 200 nm.) (C) Live/dead staining (a1, b1, and c1), and FISH (a2, b2, and c2) images. (C, a1 and a2) XH001/TM7x coculture 24 h after inoculation, with approximately two TM7x cells per XH001 cell. (C, b1 and b2) XH001/TM7x coculture 36 h after inoculation, with approximately six TM7x cells per XH001 cell. (C, b1, Inset) Live/dead staining of monoculture of XH001 36 h after inoculation. (C, c1 and c2) XH001/TM7x coculture 96 h after inoculation. For live/dead staining, live cells appear green and dead cells appear red; whereas for FISH, XH001 appears red and TM7x appears green. (D) TEM images showing the cell membrane of XH001 at/near the TM7x attachment site 24 h (a) and 36 h (b) after inoculation. (Insets) Original images from which D (a and b) are derived. (Scale bars: B, a–d and C, 1 μm; D, 200 nm.)