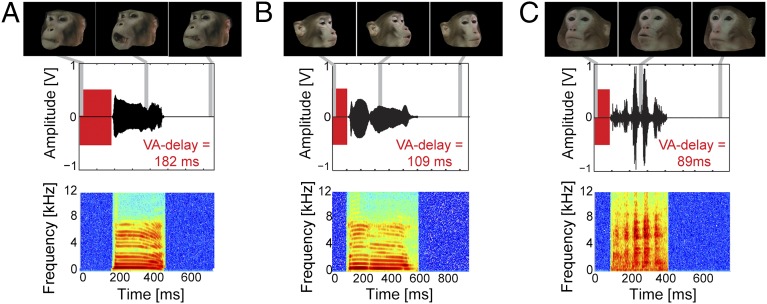
Fig. 1.
Audiovisual primate vocalizations and visual–auditory delays. (A–C) Examples of audiovisual rhesus macaque coo (A and B) and grunt (C) vocalizations used for stimulation and their respective VA delays (time interval between the onset of mouth movement and the onset of the vocalization; red bars). The video starts at the onset of mouth movement, with the first frame showing a neutral facial expression, followed by mouth movements associated with the vocalization. Gray lines indicate the temporal position of the representative video frames (top row). The amplitude waveforms (middle row) and the spectrograms (bottom row) of the corresponding auditory component of the vocalization are displayed below.