Fig. 1.
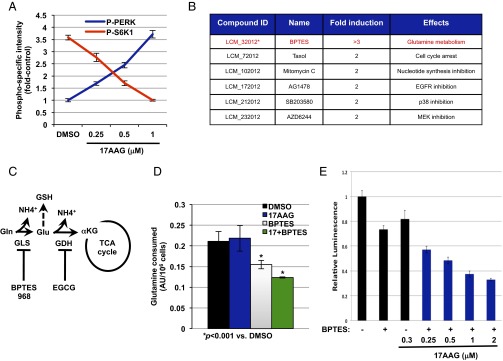
A targeted small-molecule screen identifies GLS inhibition to sensitize Tsc2−/− MEFs to Hsp90 inhibition. (A) Phosphospecific intensities for PERK and S6K1 in Tsc2−/− MEFs treated with increasing concentrations of 17AAG as indicated for 72 h. The intensities were calculated by using the LiCOR-Odyssey Infrared Imaging system. The mean is shown; error bars represent SEM (n > 3). (B) Molecules identified to sensitize Tsc2−/− to 17AAG (0.3 μM) at a cutoff of twofold. (C) A diagram showing the enzymes involved in glutamine anaplerosis and GSH production and the inhibitors used in this study (see text for more details). (D) Glutamine consumption of Tsc2−/− MEFs after 72 h of treatment with DMSO, 17AAG (0.5 μM), BPTES (10 μM), or BPTES plus 17AAG. The mean is shown; error bars represent SEM (n > 3). (E) Cell viability of Tsc2−/− MEFs using the CellTiter-Glo. Relative luminescence was measured in Tsc2−/− MEFs after 72 h of treatment with increasing concentrations of 17AAG with or without BPTES as indicated. The mean is shown; error bars represent SEM (n > 3).
