Table 3. Physicochemical and ADME Properties of 14g,n and 21g.
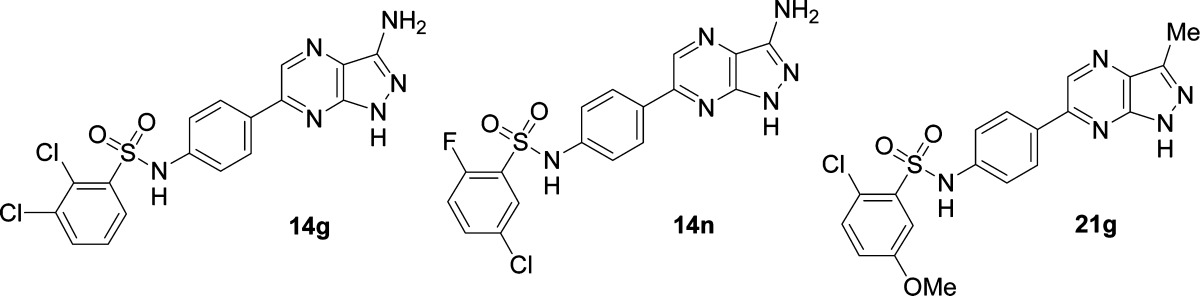
| compd | 14g | 14n | 21g |
|---|---|---|---|
| MW | 435 | 418 | 429 |
| LLE 10/500 μM ATP | 6.2/4.1 | >6.7/5.4 | 6.0/4.8 |
| LogD (pH 7.4, 25 °C) | 2.28 | 2.01 | 2.70 |
| CLogP | 4.38 | 4.09 | 4.03 |
| PSA (Å2) | 135 | 135 | 118 |
| H-bond donors | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| H-bond acceptors | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| rotatable bonds | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| aqueous solubility (pH = 7.4, 25 °C) | 0.011 mg/mL | <0.001 mg/mL | <0.001 mg/mL |
| FeSSIFb solubility (pH = 5.0, 25 °C) | 0.069 mg/mL | 0.075 mg/mL | 0.038 mg/mL |
| IC50 hSGK1 10/500 μM ATP | 0.003/0.442 μM | 0.001/0.041 μM | 0.002/0.034 μM |
| IC50 hSGK2 500 μM ATP | 0.924 μM | 0.128 μM | nd |
| IC50 hSGK3 500 μM ATP | 23.3 μM | 3.1 μM | nd |
| IC50 phosphorylation of GSK3β in U2OS cells | 1.4 μM | 0.69 μM | nd |
| metabolic degradation in human microsomesc | 14% | 8% | 27% |
| intrinsic clearance in human hepatocytes (mL/h/106 cells) | 0.051 | nd | 0.150 |
| Caco2 permeability (×10–7 cm/s) | 133 | 124 | 135 |
| CYP3A4 inhibition IC50a (M/T) | >30/14.5 μM | >30/28.6 μM | 26.8/18.6 μM |
| kinase selectivity: kinases with >50% inhibition at 1 μM | 1/60 | 0/60 | nd |
Incubated at 37 °C for 10–30 min at 0.3–30 μM. M = midazolam site; T = testosterone site.
Simulated gastric juice in the fed state.
Percent degradation after 20 min incubation (see Supporting Information for details).
