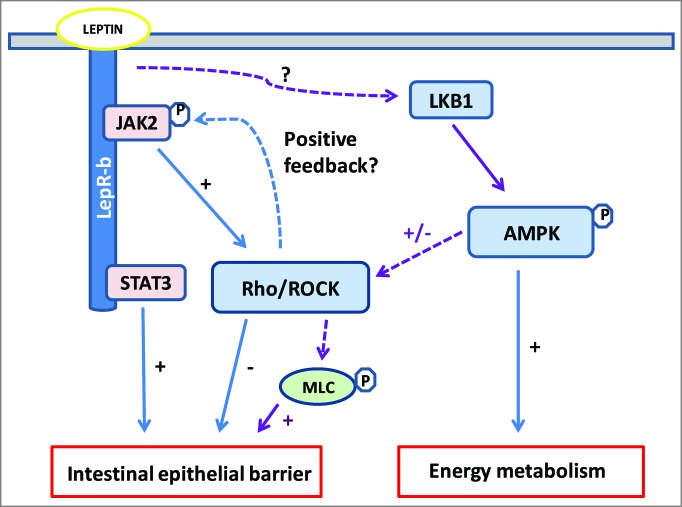
Figure 1.
Leptin signaling cascade at the crossroad of JAK/STAT3, Rho/ROCK and AMPK pathways in intestinal epithelial cell (IEC). Beneficial (+) and deleterious (-) effects of leptin upon intestinal epithelial barrier (IEB) involve the interplay of signaling pathways regulating cell metabolism and tight-junction (TJ) integrity. Leptin activates AMPK, probably via LKB, thereby stimulating IEC metabolism under physiological or cellular stress. Parallely or concomitantly, AMPK induces myosin light chain (MLC) phosphorylation, probably via Rho/ROCK, and thus regulates actomyosin contractility and TJ structure. Leptin activates RhoA/ROCK directly or via JAK, resulting in F-actin cytoskeleton reorganization and increased IEB permeability. As shown in neurons7, Rho/ROCK could activate of JAK in IEC. LepR-b signaling through the JAK2/STAT3 is important for IEB integrity and repair. See text for details. Dotted lines show hypothetical pathways.