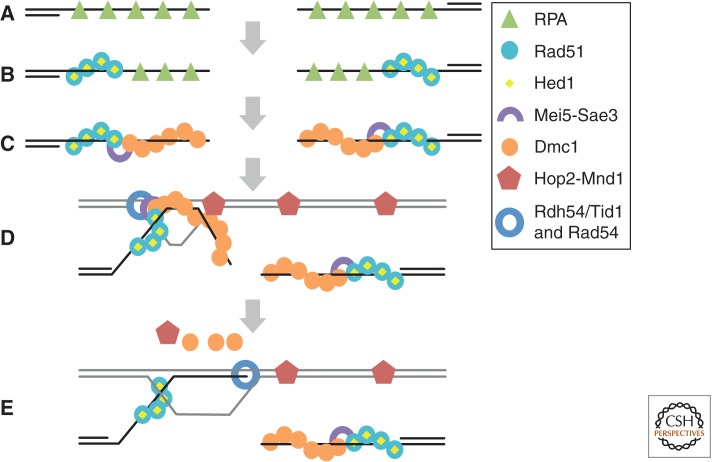
Figure 4.
Working model for assembly and function of Rad51–Dmc1 recombinosomes. (A) RPA binds to ssDNA regions formed by nucleolytic resection of DNA ends. (B) Rad51, with the aid of mediator proteins (not shown), displaces RPA. Rad51 is prevented from forming D-loops by the inhibitory protein Hed1. (C) Mei5–Sae3 promotes initiation of Dmc1 filaments at the end of a Rad51 filament. Once initiated, Dmc1 filaments elongate on DNA by homotypic protomer–protomer interactions. (D) Dmc1 carries out a homology search culminating in formation of a segment of heteroduplex DNA. Efficient formation of D-loops by Dmc1 requires interaction of the searching filament with a complex of Hop2–Mnd1 bound to the target dsDNA. (E) The Rdh54/Tid1 translocase, or the Rad54 translocase, binds the Rad51 filament and translocates along the heteroduplex, simultaneously displacing Dmc1 and extending the heteroduplex tract to the 3′ end. The end is, thus, rendered accessible for initiation of DNA synthesis.