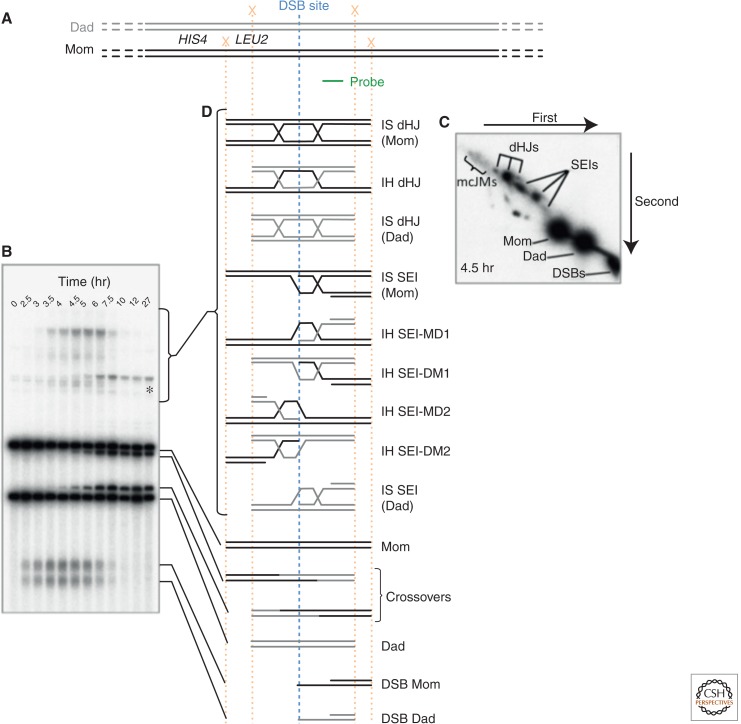
Figure 5.
HIS4::LEU2 DSB hot spot. (A) Structure of the HIS4::LEU2 DSB hot spot. The paternal and maternal homologs are shown in gray and black, respectively. A single DSB hot spot is located downstream from the LEU2 gene, which was inserted adjacent to the HIS4 locus (Cao et al. 1990). XhoI restriction endonuclease cleavage sites (X) are engineered such that cleavage of the paternal and maternal homologs yields fragments of distinct sizes on Southern blots (probe location in green). (B) A representative 1D gel, showing the structure of chromatids at the HIS4::LEU2 DSB hot spot throughout a meiotic time course experiment. *A meiosis-specific band resulting from gene conversion of the XhoI site closest to the DSB site. (C) Single time point of a representative 2D gel showing branched molecules (SEIs, dHJs, and multichromatid joint molecules [mcJMs]) migrating off of the linear arc. (D) Schematic of the various species observable at the HIS4::LEU2 DSB hot spot. Note that although both products and intermediates of meiotic recombination are observable, crosslinking of the DNA by ultraviolet light before DNA purification is required to stabilize the branched JMs. SEI nomenclature is from Kim et al. 2010. (From data in Figure 2 in Oh et al. 2007; modified, with permission.)