Figure 1.
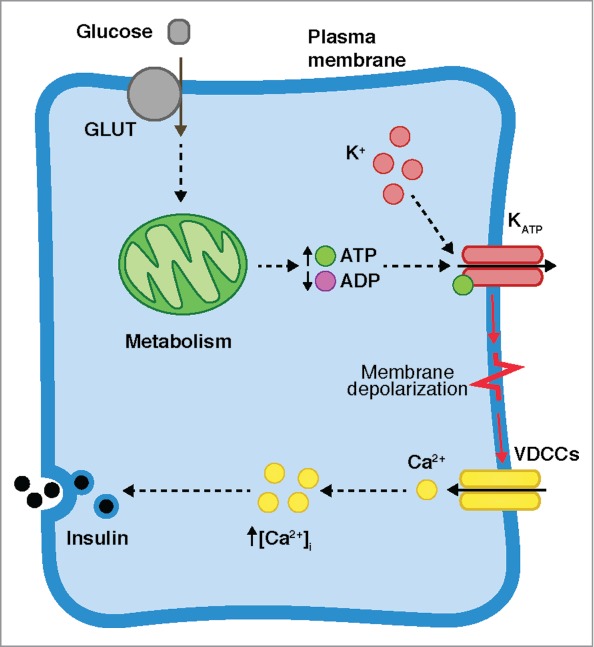
Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS). After glucose is transported into the cell by the GLUT transporters, it is metabolized, potentiating the production of ATP and the closure of the ATP-sensitive K+ channels (KATP). The membrane is depolarized and voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels (VDCCs) are activated, allowing the influx of Ca2+. The increase of the intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) stimulates Ca2+-dependent insulin secretion.
