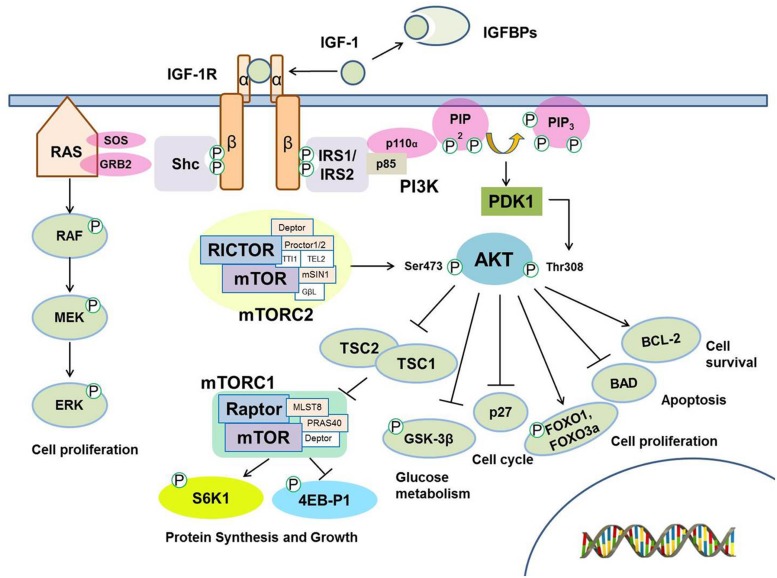
FIGURE 1.
The insulin growth factor 1 (IGF-1) signaling pathway. IGF binding proteins (IGFBPs) modulate IGF -1 bioavailability. IGF -1 functions as a ligand to interact with IGF -1 receptor (IGF -1R) in the cellular membrane, which leads to autophosphorylation and recruitment of the adaptor proteins IRS-1, IRS-2, and Shc. The interaction of IRS-1 and IRS-2 with IGF -1R induces the activation of the class I phosphatidyl inositol 3’ kinase (PI3K). PI3K converts PIP2 to the lipid second messenger PIP3. AKT family of kinases is activated by PDK1 and by mTOR-containing complex mTORC2 resulting in the phosphorylation at Threonine 308 (Thr308) and Serine 473 (Ser473), respectively. Activated AKT then regulates downstream signaling molecules including Tuberous sclerosis protein 1/2 (TSC1/2) which inhibit mTORC1 complex and regulate S6K1/2 and 4EB-P1 phosphorylation, FOXO transcription factors, GSK-3β, p27, BAD, and BCL-2. These downstream molecules are involved in several cellular processes including protein synthesis, glucose metabolism and cell survival. In parallel, Shc activation induces the activation of the RAS/MAP kinase pathway, which results in increased cell proliferation.