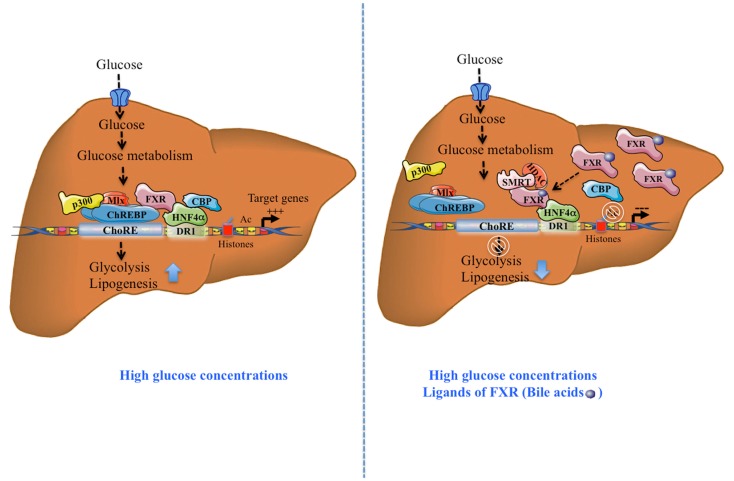
Figure 1.
Activation and transrepression of ChREBP-target genes by ChREBP and FXR. After a meal, in the presence of high glucose concentrations, without FXR activation, ChREBP binds together with HNF4α, to ChoRE region of the l-PK promoter and transactivates gene expression, in part due to the recruitment of co-activators p300 and CBP. Due to its direct interaction with ChREBP and HNF4α, FXR interacts with this complex. The complex formation leads to the stimulation of the glycolytic and lipogenic pathways. The synergistic presence of high glucose concentrations and FXR ligands (bile acids, CDCA), activated FXR recruits the co-repressor SMRT. This recruitment leads to the release of ChREBP, CBP, and p300 leading to the inhibition of ChREBP-target gene expression. Tethered to the promoter through its interaction with HNF4α, FXR recruits the transcriptional co-inhibitor SMRT and represses transcription through the recruitment of HDACs and deacetylation of H3 histones. This effect leads to inhibition of the glycolytic and lipogenic pathways.