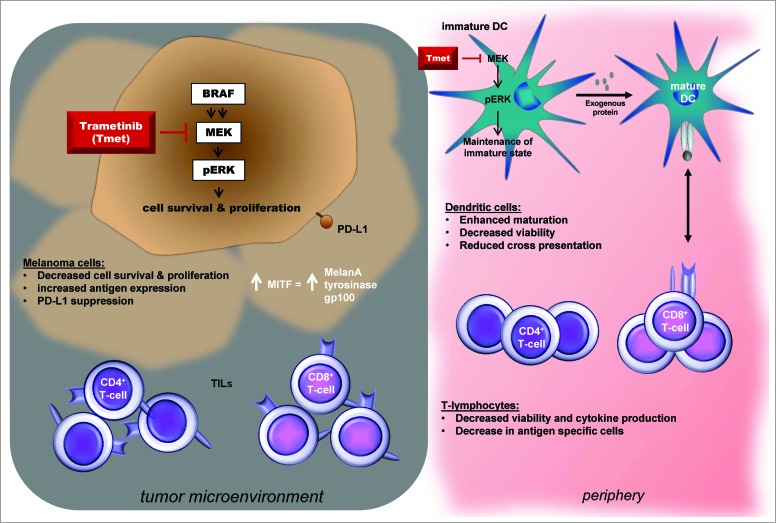
Figure 1.
Proposed consequences of MEK inhibition on tumor and immune cell populations. MEK inhibition (MEKi) increases expression of the melanoma differentiation marker MDA on melanoma cells, suppresses PD-L1 expression in vitro and can reverse the decrease in MDA and CD8+ T-cell infiltrate seen in patient tumors at the time of progression while on BRAFi. MEKi also modulates T-lymphocyte and monocyte-derived dendritic cell (moDC) function in vitro. MEKi reduces T-lymphocyte viability and proliferation and IFNγ production and cytokine secretion. Trametinib also inhibits the activation of antigen-specific T-cells, cross presentation of tumor antigens and TNFα and IL-6 production. MEKi promotes maturation of moDCs in the presence of LPS or TNFα in vitro. Further studies in vivo will be required to evaluate the potential clinical impact of these in vitro findings.