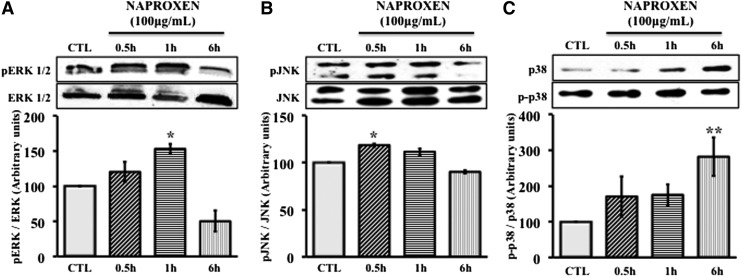
FIG. 3.
Effect of Naproxen on phosphorylation of MAPKs in normal hMSCs. Normal hMSCs were cultured to near confluence in complete DMEM. Then, the cells were serum starved for 24 h followed by treatment with Naproxen (100 μg/mL) or without (CTL) for up to 6 h. Protein expression and phosphorylation of ERK 1/2, JNK, and p38 were determined by immunoblotting and protein bands were quantified using Image J (NIH) software. Total ERK 1/2, JNK, and p38 were used to normalize corresponding phosphorylated forms. Values represent the mean±SE of three experiments. (A) Effect of Naproxen on phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). Naproxen significantly increased the phosphorylation of ERK at 1 h (153±12, *p<0.05), which reached to below control levels after 6 h (50±26). (B) Effects of Naproxen on phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). Naproxen significantly increased the phosphorylation of JNK in 0.5 h (119±3, *p<0.05), which reached to control levels after 6 h. (C) Effects of Naproxen on phosphorylation of p38. The phosphorylation of p38 increased by 30 min and this increase was statistically significant at 6 h (282±106, **p<0.01).