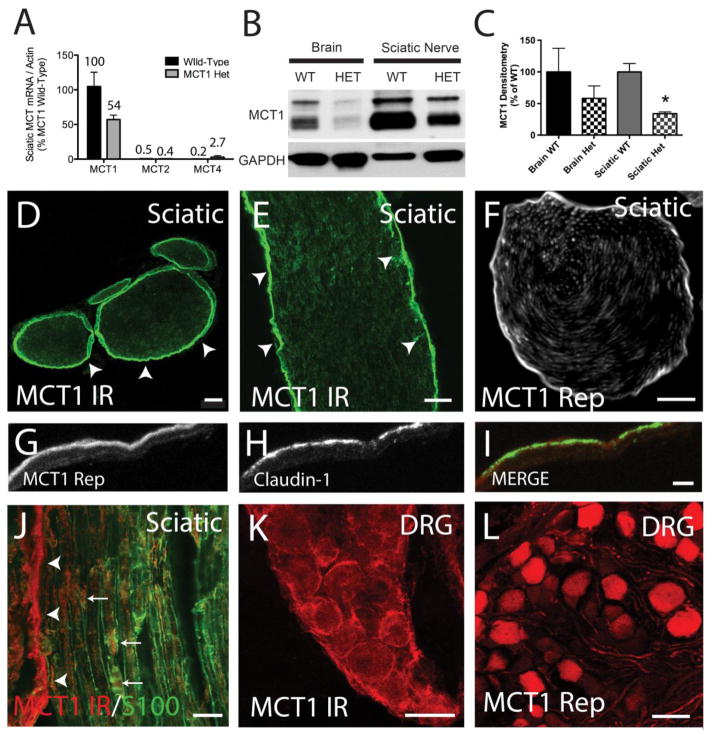
Figure 1. Localization of MCT1 in the peripheral nervous system.
(A) MCT mRNA expression by real-time RT PCR in the sciatic nerves of wild-type (WT) and MCT1 heterozygous null (MCT1 Het) mice. All values are percentages relative to MCT1 mRNA in WT mice (n=3). Western blot (B) and densitometry quantification (C) of MCT1 protein in WT and MCT1 Het mice. MCT1 immunoreactivity (MCT1 IR) in cross-section (D) and longitudinal section (E) of sciatic nerve from WT mice alone or co-localized with Schwann cell marker, S100 (J). Perineurium (D–I; arrowheads) is strongly immunoreactive, though there is some co-localization with Schwann cells (J; arrows) in mouse peripheral nerves, as well (D, E scale bars 100 μm; F scale bar 20μm). Identical to immunofluorescence, MCT1 BAC tdTomato reporter expression localizes primarily to the perineurium (F). Perineurial cells, labelled with claudin-1 immunofluorescence (green), also express tdTomato in MCT1 BAC reporter mice (G–I; red, scale bars 5 μm). Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons are immunoreactive for MCT1 (K) and positive for MCT1 BAC reporter (L; scale bars 50μm). Error bars reflect standard error of the means (S.E.M.).