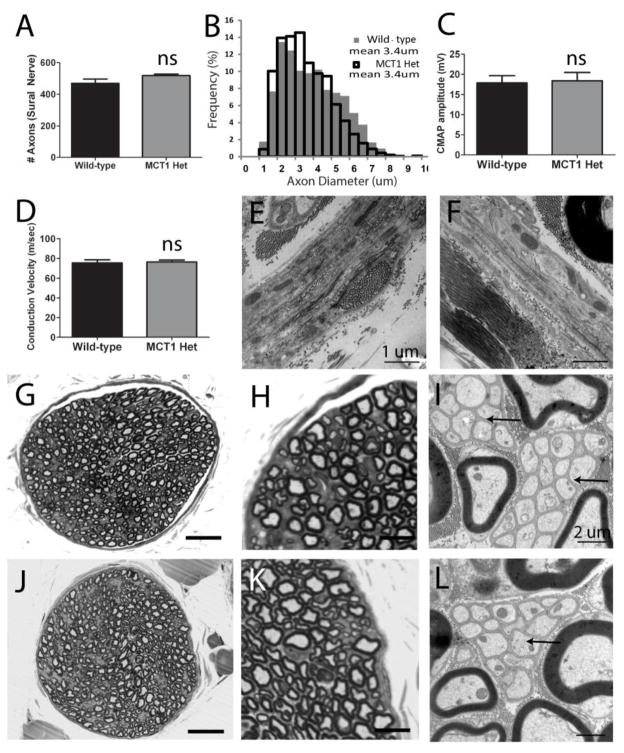
Figure 2. Morphology and electrophysiologic properties of nerves from MCT1 Heterozygous null (MCT1 Het) mice.
Quantification of axon number (A) and axon diameter (B) in sural nerve from WT (n=6) and MCT1 Het (n=4) mice. Compound motor action potential (CMAP) amplitude (C) and conduction velocity (D) following sciatic nerve stimulation in WT (n=8) and MCT1 Het (n=7) mice. Perineurium in WT (E) and MCT1 Het (F) mice (scale bars 1 μm). Photomicrographs of wild type (G–I) and MCT1 Het (J–L) sural nerves processed for light (G, H, J, K; scale bars 100 μm G, J; 10 μm H, K) and electron (I, L; scale bars 2 μm) microscopy. Arrows indicate Remak bundles of unmyelinated axons in WT (I) and MCT1 Het (L) mice. All error bars reflect S.E.M.