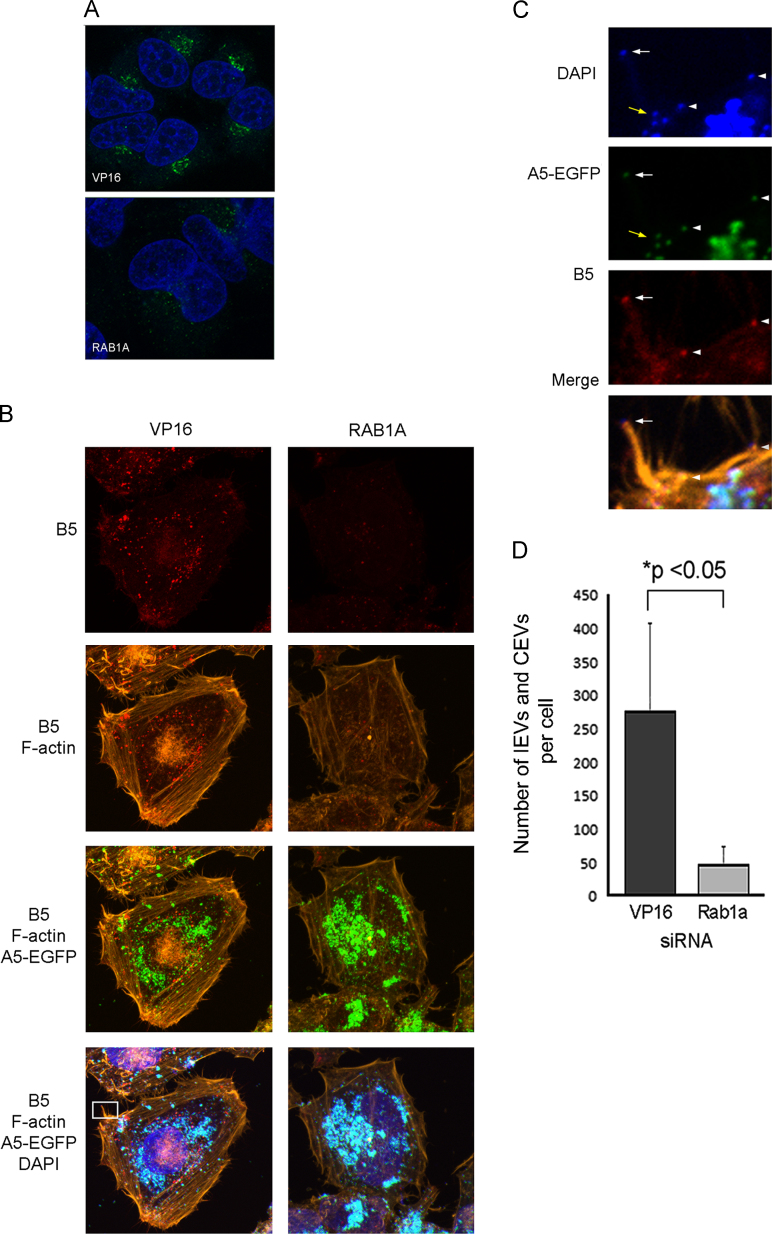
Fig. 3.
RAB1A knock down causes dispersal of the Golgi and a reduction in the number of B5-labelled virions. HeLa cells were transfected with siRNA targeting VP16 or RAB1A for 48 h then (A) infected with VACV at 5 PFU/cell for 8 h and then fixed and labelled with anti-GM130 antibody which labels the Golgi (green) and DAPI (blue). Images were acquired with a Zeiss LSM 710 confocal microscope. (B) Cells were transfected as described above then infected with VACV-A5L-EGFP (green) at 5 PFU/cell for 8 h and then fixed and labelled with anti-B5 antibody (red), phalloidin (orange), and DAPI (blue). Images are maximum intensity projections acquired with the Zeiss LSM 710 confocal microscope. The cell shown in panels on the left is representative of the population of cells transfected with nontargeting siRNA (VP16). The cell shown in panels on the right is representative of the population of cells transfected with siRNA targeting RAB1A. (C) High magnification image of the area within the white rectangle on image (B), revealing an actin tail with a CEV at the tip (white arrow), as well as a cluster of IMVs (yellow arrows) and IEV/CEVs on or near the surface of the cell (white arrowheads). (D) IEVs or CEVs (identified by red B5 staining colocalised with A5-EGFP signal) present in the cytoplasm or on the surface of cells were counted. A minimum of 10 cells per treatment were counted and the data are expressed as the average number of B5 stained virions per cell. The error bar depicts the standard deviation and P value <0.05 is indicated (t-test).