Figure 2. Agonist efficacy correlates with closure of the GluA2 ligand binding cleft.
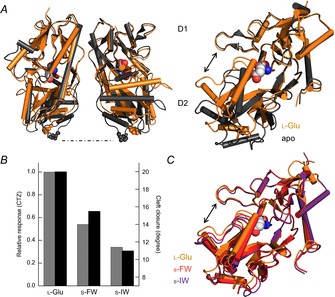
A, side view of the GluA2 LBD with apo (protein data bank (PDB) 1FTO) and l-Glu-bound (PDB 1FTJ) structures overlaid (left). The residue P632, found at the base of the D2 domain, is emphasized to illustrate how this region lifts up and separates upon agonist binding. Visualization of a single subunit highlights how the cleft between D1 and D2 is narrowed in the l-Glu-bound structure (right). B and C, in the presence of the allosteric modulator cyclothiazide (CTZ) to attenuate desensitization, agonist responsiveness correlates to the degree of closure between D1 and D2 at the ligand binding cleft. For example, willardiine series agonists with smaller halogen substituents were more efficacious and produced a greater degree of cleft closure. (Jin et al. 2003).
