Figure 1.
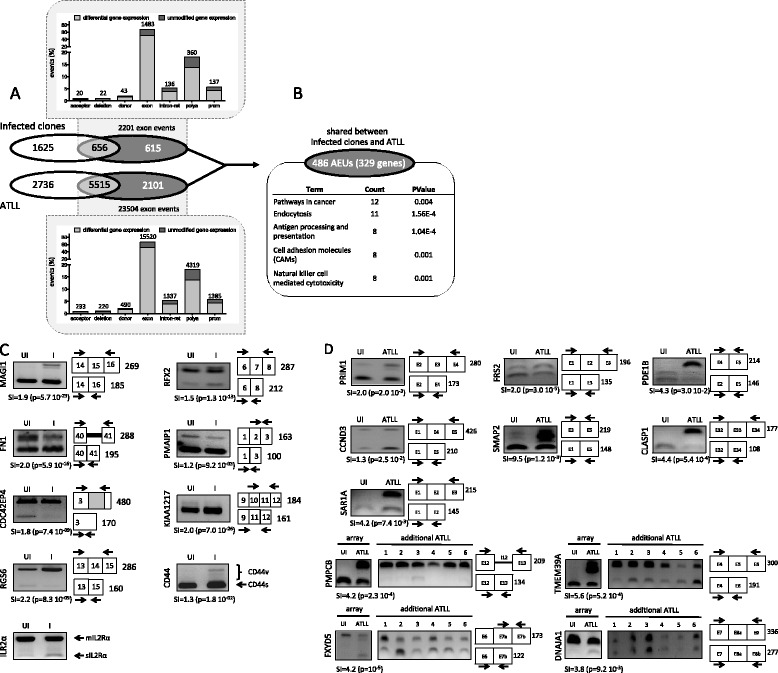
Distribution of AEU in ATLL cells and cloned CD4 + T-cells derived from HTLV-1-infected individuals. (A) Distribution of quantitative and qualitative HTLV-1 modifications in untransformed HTLV-1-positive CD4 + clones and ATLL samples. The Venn-diagrams show the distribution of genes modified at the whole gene expression level (white), AEU (dark grey), or both (light grey) in ATLL samples (bottom) and untransformed infected clones (top; six independent data sets including three PHA-activated and three unactivated clones) versus uninfected clones (six independent data sets including three PHA-activated and three unactivated clones). Graphs present the distribution of each class of AEU annotated according to the FASTERDB database [41]. Acceptor: alternative acceptor site; deletion: exon deletion; donor: alternative donor site; exon: exon skipping; intron-ret: intron retention; polya: alternative polyadenylation site; prom: alternative promoter. The total number of each class of exon event is indicated on the histogram bar. (B) GO analysis of genes (n = 329) presenting common AEUs in untransformed-infected clones and in ATLL samples (compared with uninfected clones). The complete set of genes featured in microarrays (42304 Ensembl geneIDs) was used as a reference background. Gene annotations are presented in Additional file 5: Table S3. (C) RT-PCR validation of microarray-predicted exon events in CD4 + T-cells derived from HTLV-1 carriers compared with uninfected T-cell clones. Exon-specific RT-PCR was performed with pooled RNA samples derived from six infected (I) and six uninfected (UI) clones, thereby reflecting the distribution of splice variants in all clones irrespective of activation status. Numbers indicate the expected band (bp) of PCR products, and the SI and p-value are indicated for each exon event; a SI ≥ 1.2 was considered to be a significant change in exon expression and used for comparisons. (D) RT-PCR validation of microarray-predicted exon events in ATLL cells (array) and exon-specific RT-PCR of six additional ATLL samples compared to uninfected T-cell clones.
