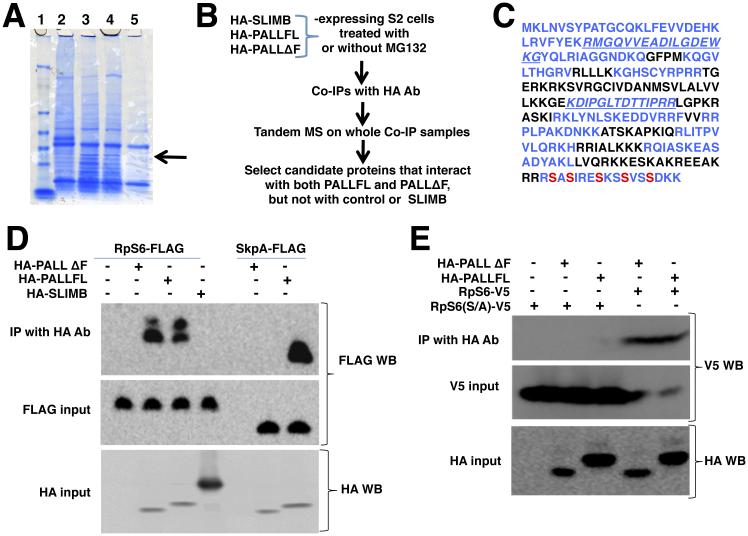
Figure 1. PALL physically interacts with phosphorylated RpS6.
(A) SDS-PAGE and coomassie blue staining of HA Ab immunoprecipitates of HA-PALLFL, HA-PALLΔF or HA-SLIMB-expressing S2 cells extracts. RpS6 identified by differential band cut-out and MALDI-TOF is indicated by an arrow. Lane 1, protein ladder; Lane 2, HA-SLIMB (unrelated F-box); Lane 3, HA-PALLFL; Lane 4, HA-PALLΔF (F-box deleted PALL); Lane 5, control S2 cells. (B) Flow chart of IPs and Tandem MS with HA-SLIMB (control irrelevant F-Box protein), HA-PALLFL and HA-PALLΔF (F-box deleted PALL) stable S2 cells. (C) Primary amino-acid sequence of endogenous RpS6. In blue are sequences found by Tandem MS. Phosphorylated S are indicated in red. (D) IPs with HA Ab of crude protein extracts from transiently transfected S2 cells expressing RpS6-FLAG or SkpA-FLAG and HA-SLIMB, HA-PALLFL, or HA-PALLΔF. RpS6-FLAG immunoprecipitates with HA-PALLFL and HA-PALLΔF but not with HA-SLIMB. As a control, SkpA-FLAG immunoprecipitates with HA-PALLFL but not HA-PALLΔF. Inputs are given by WB detection on protein extracts of RpS6-FLAG and SkpA-FLAG, or of HA-SLIMB, HA-PALLFL, and HA-PALLΔF expressing cells with FLAG and HA Abs, respectively (see also Fig. S1B)(E) IPs with HA Ab of protein extracts from S2 cells expressing RpS6-V5 or its RpS6(S/A)-V5 mutant with HA-PALLFL or HA-PALLΔF, followed by V5 Ab WB. The PALL/RpS6 interaction is lost when RpS6 is mutated at its S phosphorylation sites. See also Fig. S1.