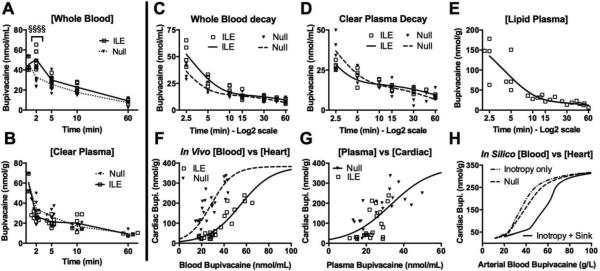
Figure 2. Intravenous partitioning of toxin.
(A) Whole blood bupivacaine concentration at 0.5 2, 5, 10 and 60 minutes (n=4 animals for 0.5min & 60 min; n=8 for others) following infusion for control (null) or ILE (ILE) demonstrating an increase in bupivacaine concentration at 2 minutes (Welch's ANOVA: F = 27.57, p<0.0001; Bonferroni post-test at 2 minutes: §§§§ p<0.0001.) (B) Same as “a” for clear plasma but demonstrating no difference in plasma bupivacaine concentrations. Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA (F=6.789, p=0.0001), all Bonferroni post-test >0.05. (C) Whole blood bupivacaine concentration from sequential samples of null and ILE fit to two-phase exponential decay (R=0.934, 0.947 respectively; n=4 sequential samples) demonstrating no difference in elimination (Extra sum of squares F-test: F=1.286, p=0.2624) but a significant drop in the redistribution constant from 0.5441 - 0.6879 min−1 (95%CI) in null to 0.3431 - 0.4335 min−1 (95%CI) in ILE (Extra sum of squares F-test: F =32.32, p<0.0001) with analogous lengthening of t1/2α in null (1.008-1.274) to ILE (1.599-2.020). (D) Same as “C” but for clear plasma (R = 0.888, 0.924 respectively, n=4 sequential samples) and demonstrating no difference in elimination or t1/2β (Extra sum of squares F-test: F=0.386, p=0.5379) but increase in redistribution constant from 0.3707-0.5746 min−1 in null to 0.5992-0.8076 min−1 in ILE (Extra sum of squares F-test: F=9.062, p=0.0043) and analogous shortening of t1/2α from 1.06-1.870 min in null and 0.8583-1.157 min in ILE. (E) Lipid plasma component from “d”, fit to two-phase decay (R=0.88, n=4 sequential samples) with a significantly smaller redistribution constant = 0.25 ± 0.03 and much longer t1/2α=2.73 (95%CI: 2.227-3.528) than for null. (F) Treatment with ILE shifts the Boltzmann-sigmoidal fit curves (R = 0.844, 0.905 for null and ILE respectively) of blood:cardiac bupivacaine rightward (Extra sum of squares F-test=50.56, p<0.0001) demonstrating an intravenous partitioning effect (n=27 for null; n=23 for ILE). (G) After removing lipid and red blood cells and comparing plasma:cardiac bupivacaine, the partitioning effect of ILE disappears (Extra sum of squares F-test: F=2.973, p=0.0629; n=22 for null; n=21 for ILE). (H) In silico cardiac vs. arterial blood bupivacaine for three models demonstrating that a partitioning effect is required for the rightward shift.