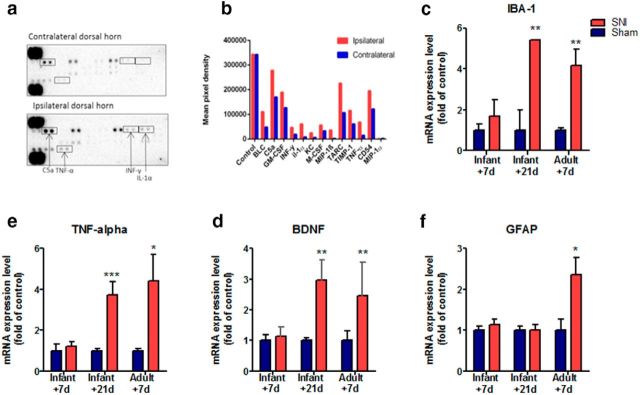
Figure 4.
A proinflammatory immune response emerges 21 d after infant nerve injury. The expression of inflammatory mediators in the ipsilateral dorsal horn spinal cord was compared with contralateral dorsal horn spinal cord tissue extracted from mice 21 d after infant SNI. a, Cytokine array blots incubated (400 μg overnight at 40C) with mouse ipsilateral dorsal horn tissue exhibit higher levels of inflammatory mediator proteins compared with those incubated with contralateral dorsal horn. b, Shows the signal (pixel density) of duplicate spots (minus an averaged background), which indicate the increase in the protein levels of many cytokines in the ipsilateral dorsal horn: BLC, CXCL13, C5a, GM-CSF, IFN-γ, IL-1α, KC, M-CSF,MIP-1β, CCL3, TARC, CCL17, TIMP-1, TNF-α, CD54, ICAM-1, MIP-1α, and CCL3. Note the control protein levels in the two arrays are comparable (average data from two replicates of one pooled sample from 5 animals). c–f, The mRNA expression of inflammatory markers was examined using real-time qPCR in ipsilateral dorsal horn tissue collected from mice 7 d after infant SNI, 21 d after infant SNI and 7 d after adult SNI, and compared with age-matched sham controls. Infant mice do not display any increase in the expression of inflammatory mediators 7 d after SNI. In contrast, 21 d after infant SNI there is an increase in (c) Iba-1, (d) BDNF, and (e) TNF-α, but not (f) GFAP compared with sham controls. An increase in these markers is also observed in adults 7 d after SNI in addition to GFAP. Data expressed as fold of sham controls ±SEM (Student's t test, IBA1: P10 + 21, n = 4, **p = 0.004; P33 + 7, n = 6, **p = 0.003; TNF: P10 + 21, n = 8 ***p = 0.001; P33 + 7, n = 5, *p = 0.03; BDNF: P10 + 21,n = 8 **p = 0.004; P33 + 7, n = 4, **p = 0.002; GFAP: P33 + 7, n = 6, *p = 0.02).