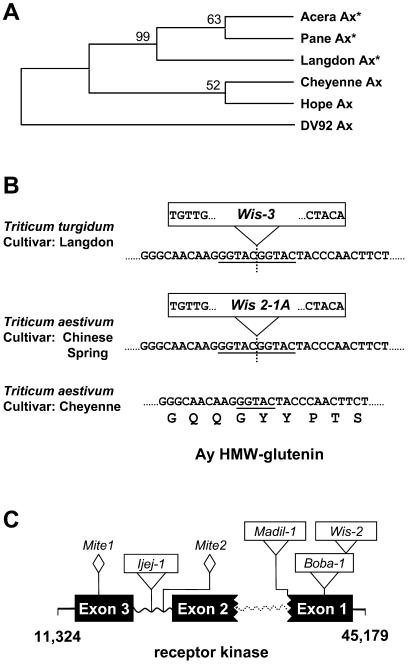
Figure 2.
Gene disruption in the Glu-A1 region. A, Phylogenic analysis on Ax HMW-glutenin coding sequences from different wheats. The phylogenic tree was built by unweighted pair-group method with arithmetic mean (UPGMA) using MEGA2 software (available at www.megasoftware.net). Cheyenne, Pane, Acera, and Hope are hexaploid wheats (T. aestivum), Langdon is the tetraploid wheat (T. turgidum) analyzed in this paper, and DV92 is a diploid wheat (T. monococcum). The Ax HMW-glutenin gene from the diploid wheat was used as a outgroup. Bootstrap values are indicated. The inactive Ax HMW-glutenin genes are labeled with stars. B, Insertion of WIS element in the Ay HMW-glutenin gene. Portions of the Ay HMW-glutenin nucleotide sequences from different wheat species or cultivars are provided. The position of the Wis-3 element insertion is indicated by a vertical dashed line. The 5-bp inverted repeat sequences of the LTRs are shown in the boxed Wis retroelements. The 5-bp region that was used as a target site duplication (TSD) is underlined in the sequences. The repeat motif encoded by the given nucleotides is provided for the Cheyenne cultivar. C, Disruption of the Leu-rich receptor kinase gene. Three exons, indicated by black boxes, were predicted based on comparison with the colinear genes in the wheat D and B genomes (Anderson et al., 2003; Kong et al., 2004). The two boxes with broken borders symbolize exons that are incomplete due to a deletion event. Wavy lines represent intron regions. The dashed wavy line indicates a deleted intron. The insertion positions of retroelements are indicated.