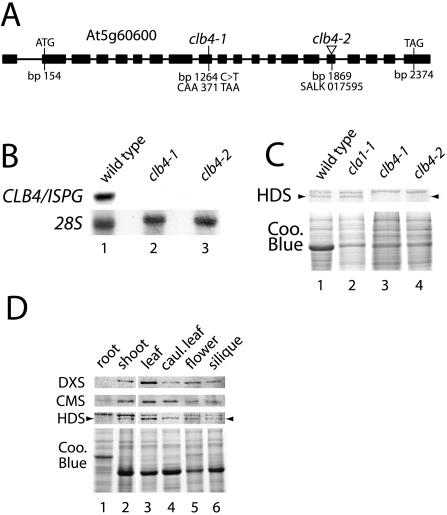
Figure 7.
CLB4 is the Arabidopsis homolog of ISPG. A, Schematic representation of the CLB4/ISPG gene from Arabidopsis. The mutations found in the ISPG gene in clb4-1 and clb4-2 alleles are shown. Filled boxes correspond to exons of the transcript. Indicated features are the translation initiation codon (ATG) and the translation termination codon (TAG). Base pairs are numbered according to the ISPG cDNA clone, GenBank accession AF434673 (Querol et al., 2002). B, Northern-blot analysis of CLB4/ISPG transcript in wild-type, clb4-1, and clb4-2 seedlings. Each lane contains 5 μg of total RNA extracted from 5-d-old seedlings. A fragment of 768 bp of the 3′ region of the ISPG cDNA was used as a probe. The membrane was rehybridized with the 28S rRNA (28S) as a loading control. C, Western-blot analysis of the HDS protein. Total protein extracts were isolated from wild-type (1), cla1-1 (2), clb4-1 (3), and clb4-2 (4) mutants. Immunoblots were perfomed using antisera made against the HDS protein. Each lane contains 10 μg of total protein extract. A Coomassie blue stained gel is shown as a loading control. D, Expression level of the HDS protein in different tissues. Total protein extracts from roots (1), shoots (2), young leaves (3), cauline leaves (4), flowers (5), and siliques (6) were used to perform an immunoblot analysis with antibodies against DXS, CMS, and HDS proteins. Ten μg of protein were loaded from each extract and the stained gel is shown as a control.