Table 5.
Fisher information matrix (FIM) predicted relative standard errors (RSEs) (%) for the hepatitis C virus model parameters with the various software tools compared with empirical RSEs
| Block diagonal FIM | Full FIM | Simulations | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | PFIM | PkStaMp/PopDes/PopED | POPT | PFIM | PkStaMp/PopDes/PopED | MONOLIX |
| βka | 12.0 | 12.1 | 13.2 | 8.6 | 8.6 | 12.2 |
| βke | 10.4 | 10.5 | 11.1 | 6.8 | 6.9 | 10.4 |
| βVd | 9.9 | 10.0 | 11.2 | 8.3 | 8.4 | 9.9 |
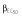 |
15.8 | 15.8 | 15.7 | 13.6 | 13.5 | 14.5 |
| βn | 10.5 | 10.4 | 10.4 | 7.4 | 7.5 | 10.6 |
| βδ | 9.5 | 9.4 | 9.4 | 8.7 | 8.5 | 10.1 |
| βc | 11.1 | 11.0 | 11.0 | 8.8 | 8.7 | 10.3 |
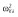 |
39.6 | 40.0 | 42.0 | 42.8 | 43.2 | 41.6 |
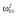 |
30.4 | 30.8 | 31.6 | 36.4 | 37.2 | 34.4 |
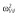 |
28.4 | 28.8 | 31.6 | 32.8 | 33.2 | 30.4 |
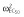 |
60.8 | 60.4 | 60.0 | 66.4 | 66.4 | 53.2 |
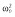 |
28.8 | 28.8 | 28.8 | 32.8 | 32.8 | 31.6 |
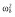 |
27.2 | 27.2 | 27.2 | 32.4 | 31.6 | 31.6 |
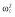 |
32.8 | 32.8 | 32.4 | 34.0 | 33.6 | 30.0 |
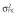 |
9.0 | 8.5 | 8.3 | 9.3 | 8.5 | 10.0 |
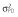 |
8.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 8.5 | 9.3 | 9.0 |
Abbreviations are as follows: c, rate constant of elimination of viral particles; EC50, drug concentration in the blood at which the drug is 50% effective; ka, rate constant of absorption; ke, rate constant of elimination; n, Hill coefficient; Vd, volume of distribution; β, fixed effects; δ, rate constant of elimination of infected cells; 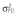 , residual variance for the pharmacodynamic response;
, residual variance for the pharmacodynamic response; 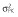 , residual variance for the pharmacokinetic response; ω2, interindividual variance
, residual variance for the pharmacokinetic response; ω2, interindividual variance
