Figure 7.
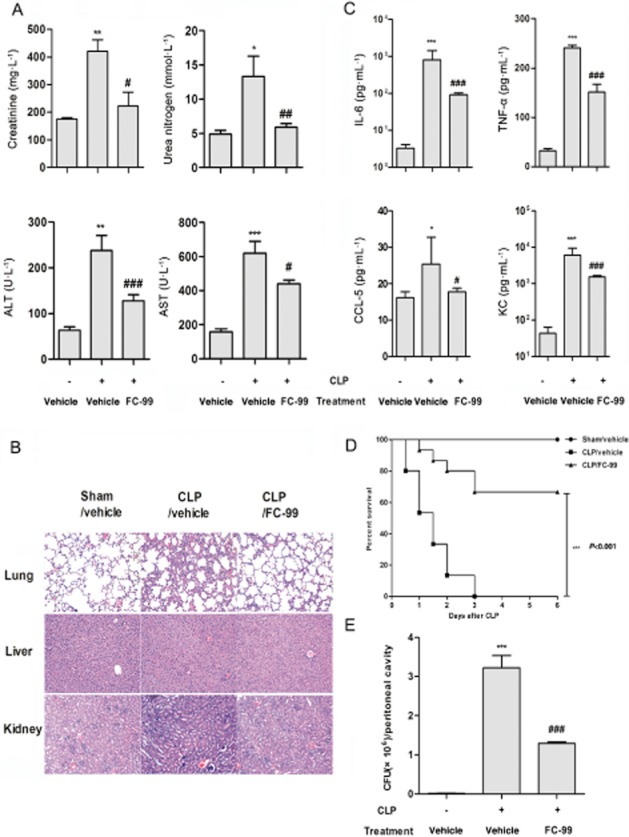
FC-99 improved survival and decreased symptoms of CLP-induced sepsis. Mice were challenged with CLP surgery after i.p. injection of FC-99 (100 mg·kg−1) or vehicle for 2 h. At 24 h after surgery, mice (n = 5 per group) were killed and the serum from each group was collected for biochemical indexes (A) including creatinine, urea nitrogen, ALT and AST, or cytokine/chemokine (C) including IL-6, TNF-α, CCL5 and KC analysis. (B) Lung, liver and kidney sections were subjected to H&E staining. (E) The numbers of bacterial colony forming units (CFU) in peritoneal lavage fluids were quantified. (D) In separate experiments (n = 15 per group), the survival rate was monitored for 6 days. The data are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus sham/vehicle group; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 versus CLP/vehicle group.
