Figure 2.
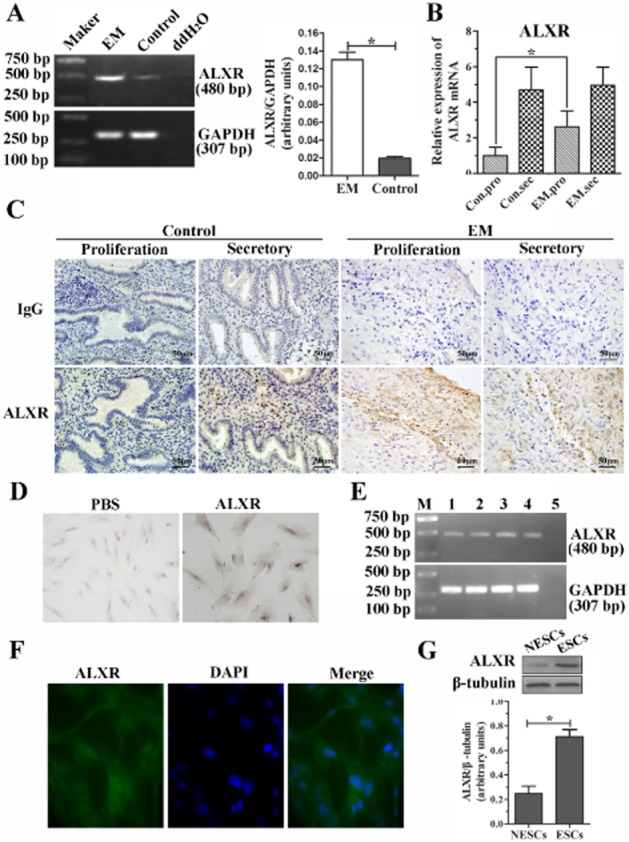
ALX receptor mRNA and protein are increased in endometriotic tissues and ESCs. (A) RT-PCR amplification of a 480 bp fragment from ectopic endometrial tissues and normal endometrium. Densitometric analysis of results are shown in column graph. (B) The ALX receptor mRNA expression was verified further in both control (n = 20) and ectopic endometrial tissues (n = 27) by real-time RT-PCR. The mRNA expression of ALX receptors was significantly greater in the EM group (n = 8) versus control group (n = 9) in the proliferative phase, but no difference was found in the secretory phase, *P < 0.05. (C) Immunohistochemical staining for ALX receptor in the human endometriotic tissues (EM, n = 12) and normal endometrium (control, n = 10). Sections were immunostained with anti-human ALX receptor antibody (ALXR) and IgG, scale bar = 50 μm. (D and E) Expression of ALX receptors in ESCs detected by immunocytochemical staining (D, ×400), RT-PCR (E), and immunofluorescence assay (F, ×400). (G) Western blot analysis of ALX receptor protein expression between normal (NESCs) and ectopic ESCs. A ratio of ALX receptor to β-tubulin was determined following densitometric measurements of the specific protein bands. Values are the mean ± SEM of the combined data from three independent experiments; *P < 0.05.
