Figure 6.
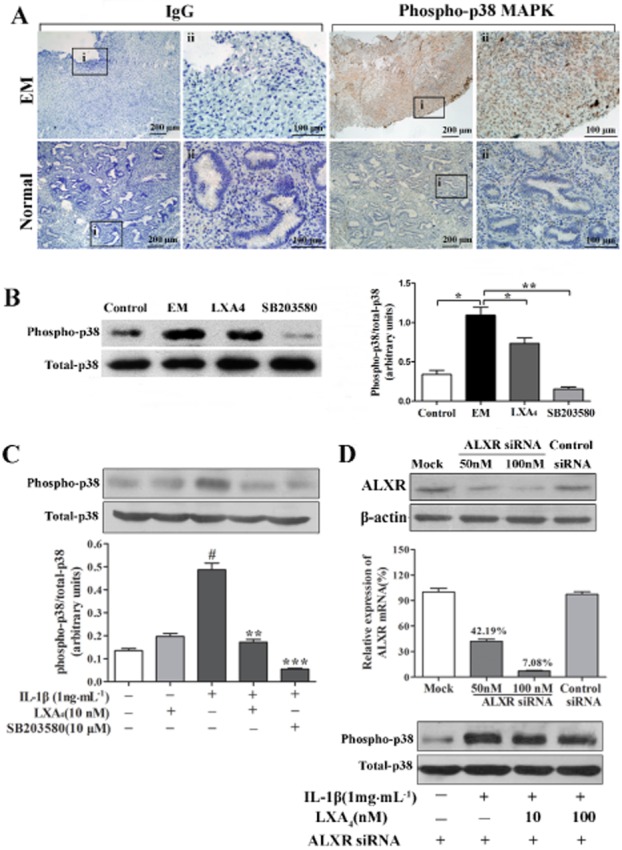
LXA4 inhibition of IL-1β-induced phosphorylation of p38 MAPK in ESCs is ALX receptor-dependent. (A) Immunohistochemical staining for phosphorylated p38 MAPK in ectopic endometrial tissues (EM, n = 12) and normal endometrial tissues (control, n = 10). Sections were immunostained with phosphorylated p38 MAPK (phospho-p38 MAPK) antibody and IgG. Original magnification: (i) ×100 and (ii) ×400. (B) A representative Western blot result demonstrated that expression of phospho-p38 MAPK was inhibited by LXA4 in peritoneal cells of EM mice. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (C) IL-1β-induced p38 MAPK phosphorylation was inhibited by LXA4. ESCs were pre-incubated with LXA4 for 30 min before IL-1β treatment for an additional 15 min. The band intensities were analysed using Quantity One software. #P < 0.001 (compared with vehicle); **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (compared with IL-1β alone). (D) ALX receptor knockdown with siRNA blocked the inhibitory effect of LXA4 on IL-1β-induced p38 MAPK phosphorylation in ESCs. Cells were transiently transfected with siRNA duplexes for the ALX receptor or scrambled siRNA (control) for 48 h. ALX receptor mRNA and protein levels significantly decreased in the presence of ALX receptor siRNA (D) Mock: the cells were transfected with transfection reagent alone. A representative Western blot result showed that LXA4 had no effect on IL-1β-induced p38 MAPK phosphorylation in ESCs transfected with ALX receptor siRNA. Experiments were repeated in ESCs from at least three different subjects.
