Figure 1.
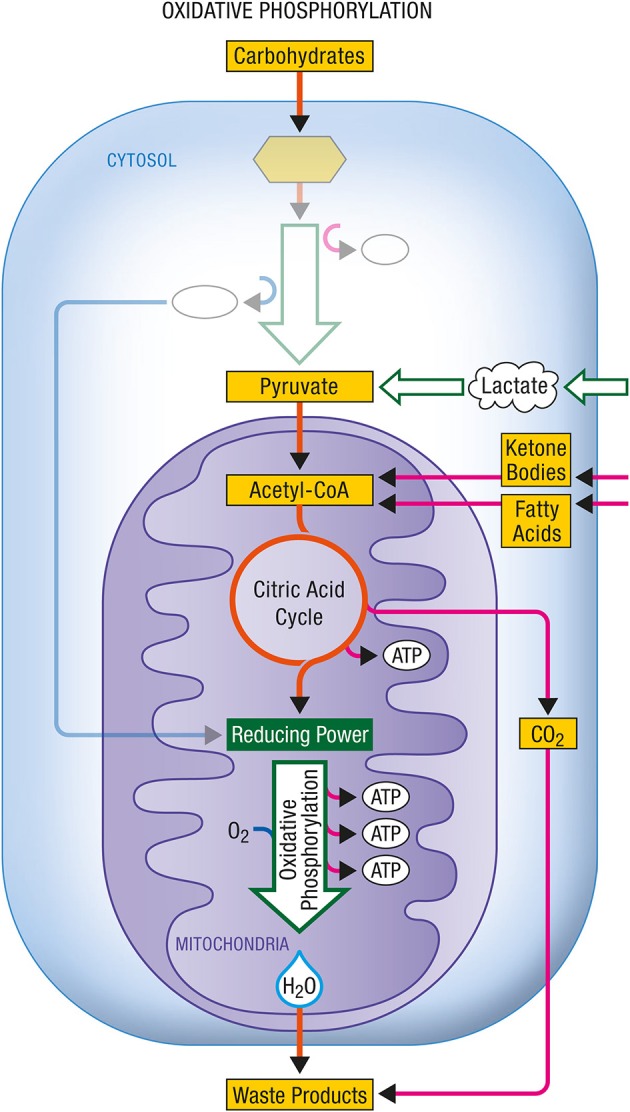
Oxidative phosphorylation. Coupled to the citric acid cycle, oxidative phophorylation allows the oxidative degradation and energy production from various energy substrates which include carbohydrates (in particular glucose after its conversion into pyruvate via glycolysis), lactate, ketone bodies or fatty acids. Both citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation take place within mitochondria and give rise to carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) as waste products. ATP, Adenosine triphosphate.
