Figure 2.
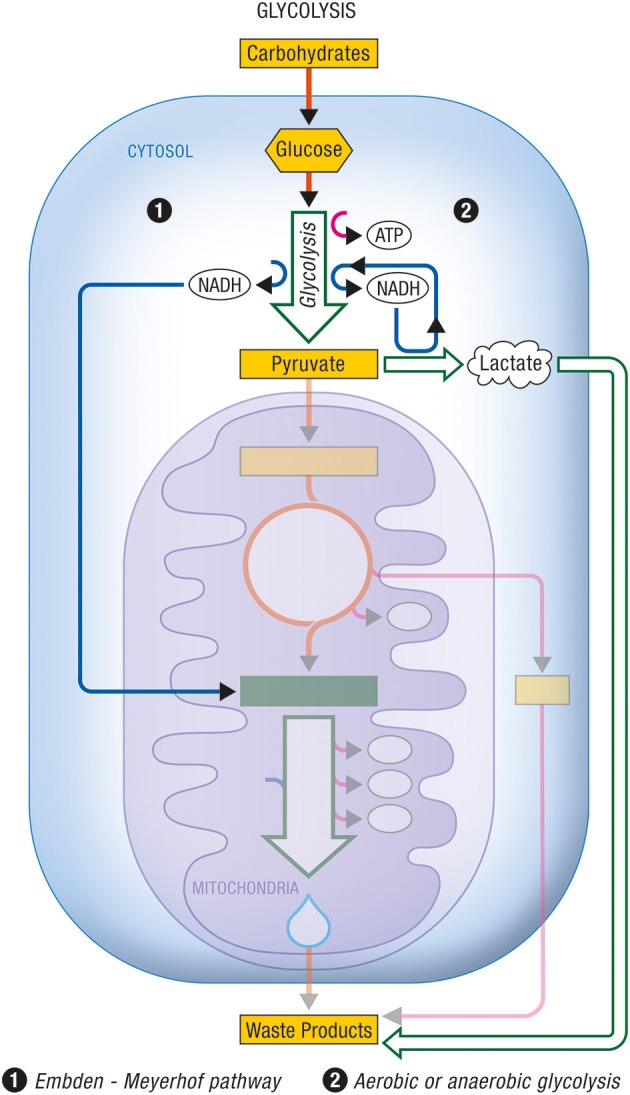
Glycolysis. Glycolysis is the non-oxidative part of the metabolic pathway that allows the use of carbohydrates by eukaryotic cells. (1) The Embden-Meyerhof pathway refers to the non-oxidative conversion of glucose (a major carbohydrate) into pyruvate prior to its entry into the citric acid cycle and its subsequent oxidation. Cytosolic NADH is reoxidized into NAD+ through specific mitochondrial shuttles. (2) Anaerobic glycolysis represents the conversion of glucose into lactate as an end product under conditions of limited oxygen availability. Aerobic glycolysis describes the same metabolic production of lactate as end product from glucose despite adequate oxygen availability to normally carry on complete oxidation of pyruvate. In these cases, cytosolic NADH is reoxidized within the cytosol by the conversion of pyruvate into lactate via the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase. ATP, Adenosine triphosphate; NADH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (reduced form).
