Figure 8.
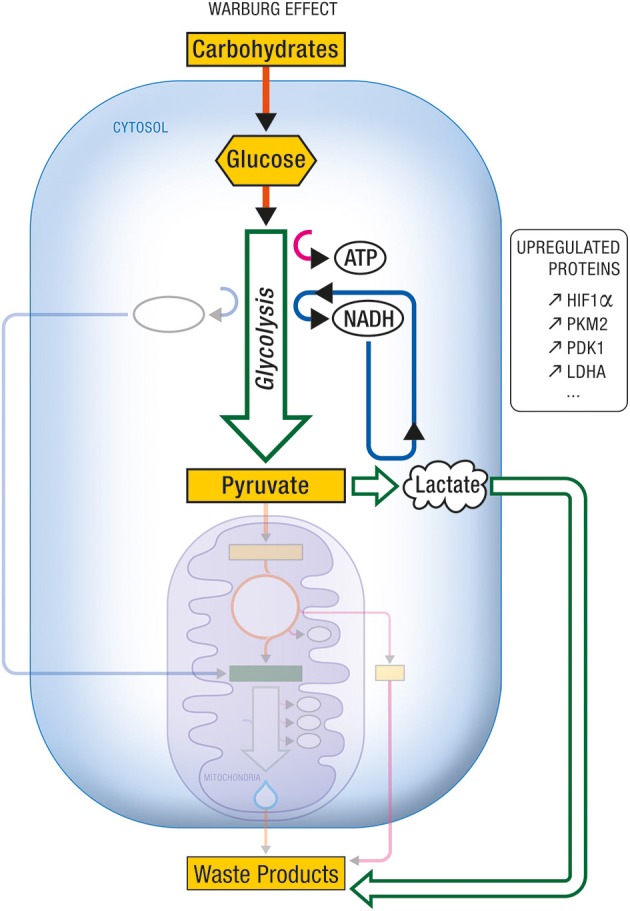
Warburg effect. Under certain conditions (e.g., tumorigenicity, proliferation), aerobic glycolysis becomes the predominant form of carbohydrate metabolism and energy production, at the expense of citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. One characteristic of this metabolic imbalance is the upregulation of several proteins and enzymes involved in glycolysis and/or in its regulation. Among others, they include the transcription factor HIF-1α, or the enzyme isoforms PKM2, PDK1, and LDHA. ATP, Adenosine triphosphate; HIF-1α, Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α; LDHA, Lactate dehydrogenase A; NADH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (reduced form); PDK1, Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1; PKM2, Pyruvate kinase M2.
