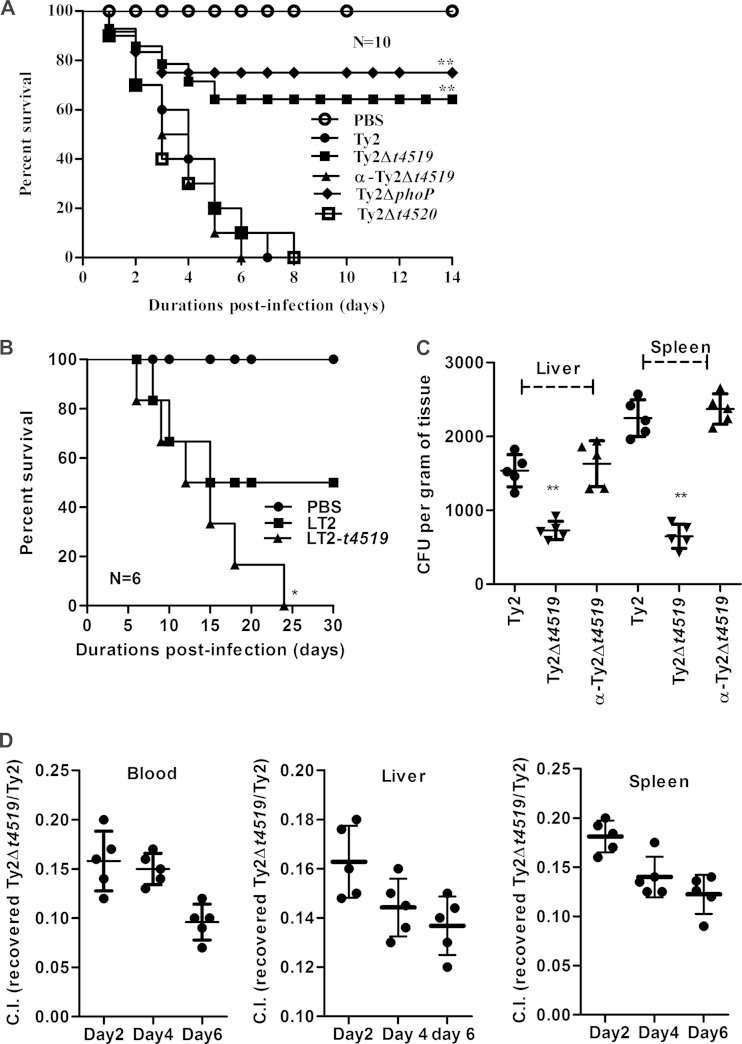
FIG 5.
T4519 promotes Salmonella Typhi pathogenesis in mice. (A) Kaplan-Meier survival plot following oral infection of BALB/c mice (8 to 10 weeks old) with 107 CFU of the indicated strains. (B) Survival plot for BALB/c mice after oral infection with 106 CFU of S. Typhimurium LT2 or a T4519-expressing LT2 strain. For panels A and B, asterisks indicate significant differences (**, P < 0.01) from results for Ty2 infection (A) or LT2 infection (B) by a log rank curve comparison test. (C) Groups of BALB/c mice were orally infected with sublethal doses (5 × 105) of the indicated bacterial strains. Visceral organs were harvested 2 days postinfection, and intracellular CFU counts were carried out after lysis of the cells. Horizontal bars represent mean CFU counts for all mice in one out of two independent experiments. Asterisks indicate significant differences (**, P < 0.01) from results for Ty2 infection as evaluated by the Mann-Whitney test. (D) Groups of BALB/c mice were orally infected with a premixed dose of the Ty2 and Ty2Δt4519 strains (2.5 × 105 CFU each). Blood and visceral organs were harvested at the indicated days postinfection. The intracellular CFU count of each strain was calculated, and results were plotted as a competitive index (C.I.). Data are representative of results of three independent experiments.