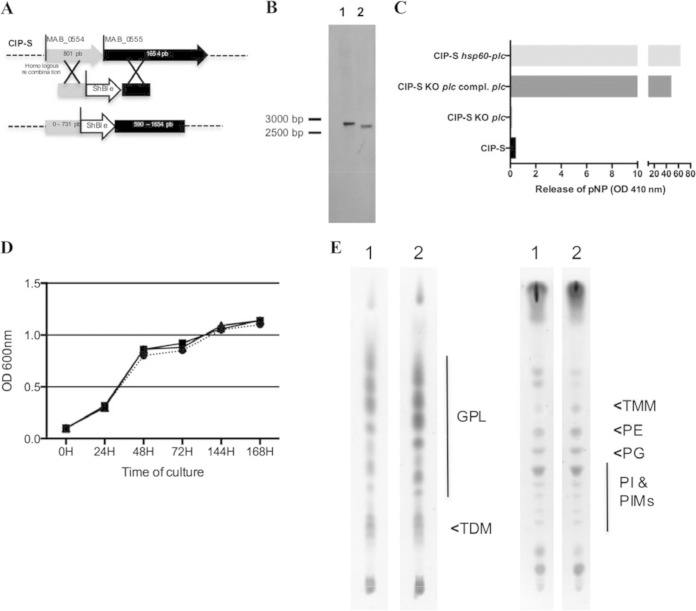
FIG 2.
Construction of the M. abscessus plc KO mutant by homologous recombination (HR). (A) MAB_0554 and MAB_0555 are separated by 4 bp. The M. abscessus plc KO mutant was thus constructed by amplifying a nearly 2-kbp M. abscessus fragment encompassing this region and cloning the zeocin resistance gene (S. hindustanus ble) into the HindIII (position 731 in MAB_0554)-ClaI (position 590 in MAB_0555) sites. The entire fragment was then electroporated into M. abscessus CIP-S containing the pJV53 plasmid inserted by HR into the M. abscessus chromosome. (B) Southern blotting analysis was performed after genomic DNA restriction by KpnI and gel electrophoresis. A 532-bp probe targeting the 3′ conserved region of MAB_0555 was used for hybridization with DNA fragments: a 2,704-bp band is observed with the WT strain (lane 1), and a 2,635-bp band is observed with the M. abscessus KO mutant (lane 2). (C) Respective PLC activity of the different constructed M. abscessus strains. Phospholipase C activity was measured with p-NPPC for the CIP-S, CIP-S plc KO, CIP-S plc KO plc-complemented, and CIP-S-hsp60-plc (M. abscessus pMVZ361-hsp60pro-MAB_0555, used as a control for PLC activity) strains. (D) In vitro growth curves estimated by spectrophotometry (OD600) of CIP-S (circles), CIP-S plc KO (squares), and CIP-S plc KO plc-complemented (triangles) strains. (E) Glycolipid and phospholipid patterns of the different constructed M. abscessus strains. Total lipid contents of the WT M. abscessus strain (lanes 1) and the plc KO M. abscessus mutant (lanes 2) were analyzed by TLC using CHCl3-CH3OH (90:10, vol/vol) (left) and CHCl3-CH3OH-H2O (60:35:8, vol/vol/vol) (right) as the solvent systems and anthrone revelation (GPLs, glycopeptidolipids; TDM, trehalose dimycolate; TMM, trehalose monomycolate; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PG, phosphatidylglycerol; PI, phosphatidylinositol; PIMs, phosphatidylinositol mannosides).