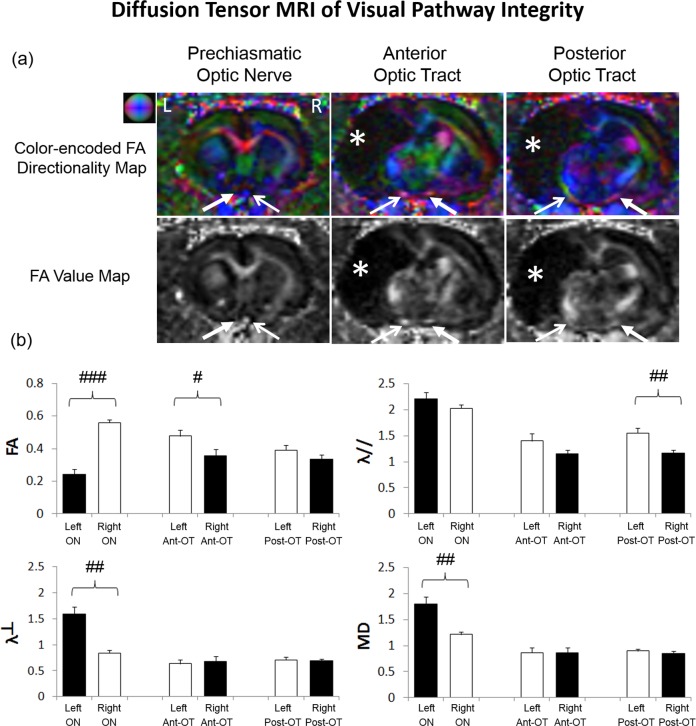
Figure 5.
Diffusion tensor MRI (DTI) of structural integrity in the prechiasmatic ON, anterior optic tract (OT), and posterior OT at 1 year after unilateral neonatal hypoxic-ischemic injury at postnatal day 7. (a) Color-encoded fractional anisotropy (FA) directionality maps and FA value maps in coronal view showed lower FA in the ipsilesional left ON than the contralesional right ON. The contralesional right anterior OT projected from ipsilesional left eye also had apparently lower FA than the opposite hemisphere. (Representative colors for different directions in color-encoded FA directionality map: blue, caudal-rostral; red, left-right; and green, dorsal-ventral; closed arrows, visual pathway projected from ipsilesional eye to ipsilesional ON and contralesional OT; open arrow, visual pathway projected from the contralesional eye to the contralesional ON and ipsilesional OT; white asterisks, brain lesion.) (b) Quantitative analysis of DTI-derived parameters in the prechiasmatic ON, anterior OT (Ant-OT), and posterior optic tract (Post-OT) of the ipsilesional left and contralesional right hemispheres. The ipsilesional prechiasmatic ON possessed 56% lower FA, 90% higher radial diffusivity (λ⊥) and 48% higher mean diffusivity (MD) than the contralesional ON (two-tailed paired t-tests, ##P < 0.01; ###P < 0.001). The contralesional anterior OT possessed 26% lower FA than the opposite hemisphere (two-tailed paired t-test, #P < 0.05). The contralesional posterior OT possessed 38% lower axial diffusivity (λ//) than the opposite hemisphere (two-tailed paired t-test, ##P < 0.01). Black bars refer to visual pathway projected from the ipsilesional eye to ipsilesional ON and contralesional OT. White bars refer to visual pathway projected from the contralesional eye to the contralesional ON and ipsilesional OT. Units for λ//, λ⊥, and MD: μm2/ms; no unit for FA.