Figure 4. Morphological characteristics of carcinoma A431 xenografts in mice.
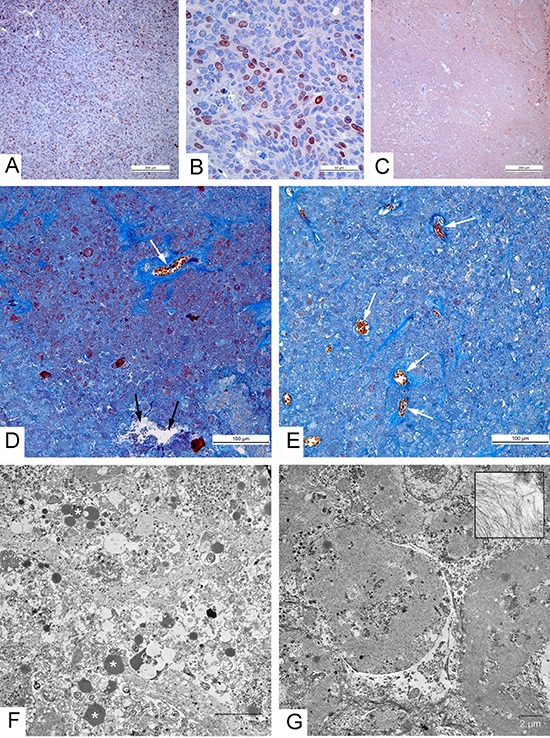
(A-C) Immunohistochemical reaction for the Ki-67 protein. (A) High proliferative activity of tumor cells in xenograft injected with saline; (B) Positive reaction for the Ki-67 protein in nuclei of carcinoma A431 cells, 2 days after injection with the L-IVP strain; (C) Negative staining in tumor, indicating absence of proliferating cells on day 36 after injection with VVdGF-ApoS24/2 strain; paraffin sections, AEC chromogen, counterstaining with hematoxylin. (D-G) 36 days after injection of the viruses. (D, E) Paraffin sections, Picro-Mallory staining. (D) Cell debris in the tumor injected with the L-IVP strain, (E) unstructured material in tumor injected with VVdGF-ApoS24/2 strain. Both photos: blue staining indicates collagen fibers, black arrows show cavity and white arrows show blood vessels; brown clumps represent cell debris stained by hematoxiline. (F, G) Representative electron micrographs showing the same areas of tumors injected with L-IVP strain (F) and VVdGF-ApoS24/2 strain (G). Masses of cell debris are present on photo F, lipid droplets are shown by asterisks. Photo G shows cell “shades” separated with streaks of cell debris. The box shows filaments at large magnification.
