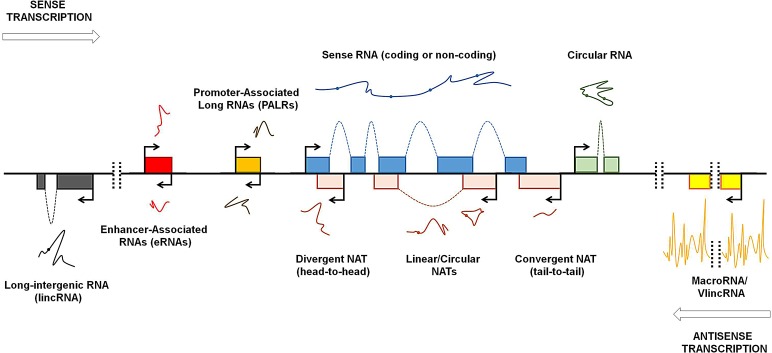
Figure 1. Genomic organization of lncRNAs.
Pervasive transcription of the genome occurs bidirectionally (arrows). Exons are schematically represented with colored boxes. Spliced transcripts are represented with lines; spots represent splice sites. LncRNAs that are transcribed from loci distinct from the sense transcript-encoding gene loci (protein-coding or non-protein-coding) are named long intergenic non-coding RNAs (lincRNAs). Exceptionally long lncRNAs are named macroRNAs and very long intergenic non-coding RNAs (vlincRNAs). Bidirectional transcription from the enhancer and promoter regions generates enhancer-associated RNAs (eRNAs) and promoter-associated long RNAs (PALRs), respectively. Antisense transcription can generate natural antisense transcripts (NATs) with varying degrees of overlap. NATs can overlap with sense transcripts at their 5′-ends (divergent NAT or head-to-head) or 3′-ends (convergent NAT or tail-to-tail). NATs and other lncRNAs can be expressed in linear or circular form. Modified with permission from Kung et al [4].