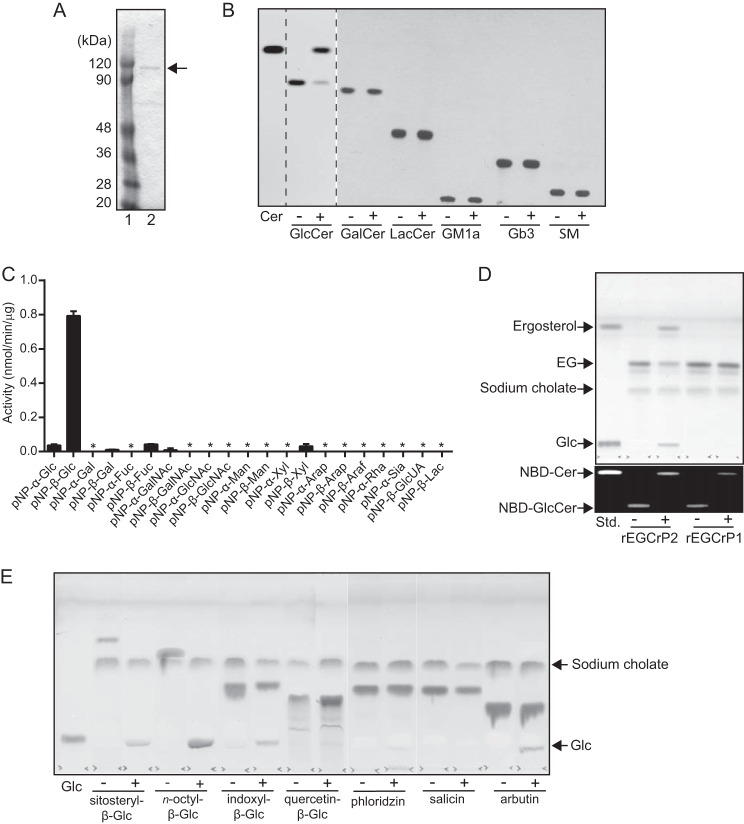
FIGURE 3.
Purification and characterization of the recombinant EGCrP2. A, final preparation of rEGCrP2 on 10% SDS-PAGE. The protein eluted from the nickel-Sepharose column was purified using Superdex 200 10/300 GL. Lane 1, protein marker; lane 2, final preparation. B, TLC showing the specificity of EGCrP2 toward various NBD-GSLs. Each NBD-GSL (100 pmol) was incubated in 20 μl of 50 mm MES buffer, pH 6.0, with 100 ng of rEGCrP2 (+) or heat-inactivated EGCrP2 (−) at 30 °C for 16 h, except for C6-NBD-GlcCer, which was incubated at 30 °C for 1 h. Samples were loaded onto a TLC plate, which was developed with chloroform/methanol/water (65:25:4, v/v/v). C, hydrolysis of pNP substrates by rEGCrP2. Error bars, S.D. of three experiments. An asterisk indicates no hydrolysis of pNP substrates. D, top TLC shows hydrolysis of EG by rEGCrP2. Fungal EG, purified from 2-mg dry cells of 2KO, was incubated at 30 °C for 18 h with 40 μg of EGCrP1 or 20 ng of EGCrP2. TLC was developed with chloroform/methanol/water (65:16:2, v/v/v) and stained with orcinol sulfate reagent. The bottom TLC shows C6-NBD-Cer released from C6-NBD-GlcCer by rEGCrP1 and -2. 50 pmol of C6-NBD-GlcCer was incubated at 30 °C with 40 μg of rEGCrP1 and 20 ng of rEGCrP2 for 18 h. +, with EGCrP2; −, without EGCrP2. E, TLC showing the hydrolysis of various β-glucosides by rEGCrP2. Each 100 nmol of substrate was incubated at 30 °C with 100 μg of enzyme for 18 h. Samples were loaded onto a TLC plate, which was developed with chloroform/methanol/water (65:25:4, v/v/v) and visualized by orcinol sulfate reagent. Glc, glucose released from various β-glucosides by rEGCrP2. +, with EGCrP2; −, without EGCrP2.