FIGURE 8.
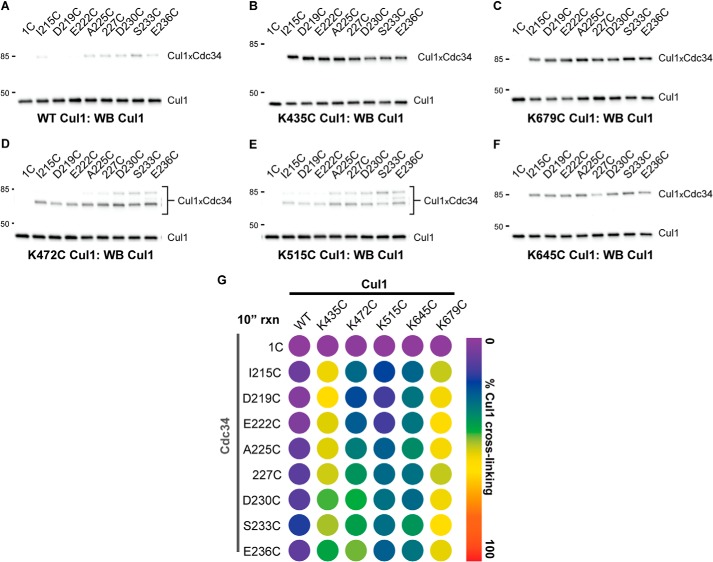
Conducting the BMOE-induced cross-linking reactions with a shorter incubation period reveals the greater reactivity of K679C and K435C Cul1-Rbx1 complexes with the Cdc34 2C proteins in comparison with the other Cul1 mutants. Cross-linking was performed in the presence of BMOE-activated Cdc34 proteins for 10 s prior to quenching. A, Cul1 Western blot of reactions between either Cdc34 1C or Cdc34 2C proteins and WT Cul1-Rbx1 in the presence of BMOE. Note that very little product is formed between the Cdc34 2C proteins and WT Cul1 (compare with Fig. 4D). B, same as A, except with K435C Cul1-Rbx1. C, same as A, except with K679C Cul1-Rbx1. D, same as A, except with K472C Cul1-Rbx1. E, same as A, except with K515C Cul1-Rbx1. F, same as A, except with K645C Cul1-Rbx1. G, heat map for the values of the fraction of Cul1 converted to Cdc34-Cul1 cross-links. Similar to Fig. 6, in cases where more than one Cdc34-Cul1 product is observed, the values for the fraction converted have been combined. Values represent the average from duplicate measurements.