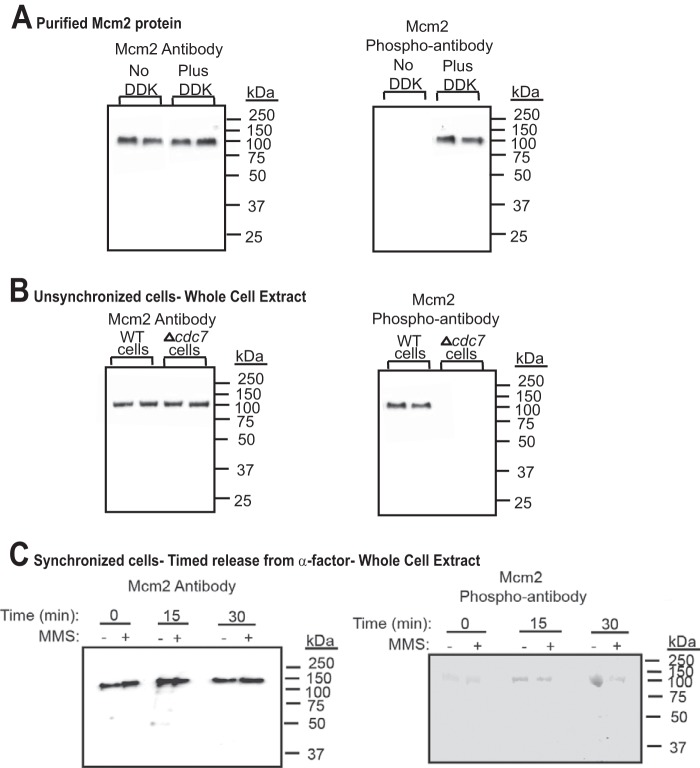
FIGURE 1.
Dbf4-Cdc7 phosphorylates Mcm2 in budding yeast cells under normal growth conditions. A, left panel, antibody raised against Mcm2 (1-160) was used to probe purified Mcm2 protein that was either unphosphorylated, or phosphorylated by Dbf4-Cdc7 (DDK). Western analysis is shown with position of molecular mass markers to the right of the gel. Duplicate experiments are shown. Right panel, antibody raised against phospho-Mcm2 (Mcm2-161-173,164-phosphoserine,170-phosphoserine) was used to probe purified Mcm2 protein that was either unphosphorylated, or phosphorylated by Dbf4-Cdc7 (DDK). Duplicate experiments are shown. B, left panel, antibody raised against Mcm2 (1-160) was used to probe whole cell extracts from unsynchronized wild-type budding yeast cells or budding yeast cells deleted for cdc7 (Δcdc7, mcm5-bob1). Duplicate experiments are shown. Right panel, antibody raised against phospho-Mcm2 (Mcm2-161-173,164-phosphoserine,170-phosphoserine) was used to probe whole cell extracts from wild-type budding yeast cells or budding yeast cells deleted for cdc7 (Δcdc7, mcm5-bob1). Duplicate experiments are shown. C, left panel, antibody raised against Mcm2 (1-160) was used to probe whole cell extracts from budding yeast cells synchronized with α-factor and then released into medium lacking α-factor for the times indicated. The experiment was performed in the absence and presence of 0.1% MMS. Right panel, antibody raised against phospho-Mcm2 (Mcm2-161-173,164-phosphoserine,170-phosphoserine) was used to probe whole cell extracts from budding yeast cells synchronized with α-factor and then released into medium lacking α-factor for the times indicated. The experiment was performed in the absence and presence of 0.1% MMS.