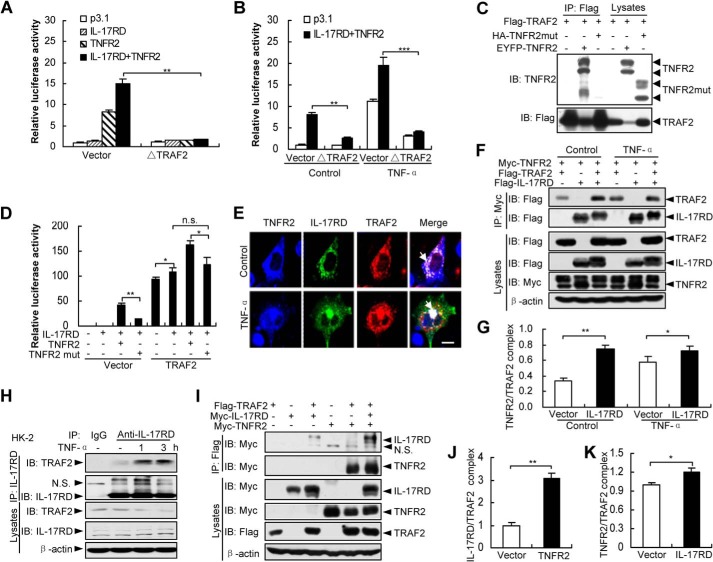
FIGURE 6.
IL-17RD coordinates with TNFR2 to recruit TRAF2. A and B, TRAF2 is required for the IL-17RD·TNFR2 complex-mediated NF-κB transcriptional activity. HEK293T cells co-transfected with indicated plasmids were stimulated without (A) or with TNF-α (B). The luciferase activity was analyzed. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. C, TNFR2mut fails to interact with TRAF2. An IP experiment was performed for HEK293T cells. IB, immunoblot. D, TNFR2mut cannot cooperate with IL-17RD to activate the NF-κB transcriptional activity. HEK293T cells co-expressed with the indicated plasmids. The luciferase activity was analyzed. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. n.s., not significant. E, co-localization of the IL-17RD·TNFR2·TRAF2 ternary complex. COS-7 cells transfected with indicated plasmids were stimulated without (Control) or with TNF-α and analyzed by double immunostaining with anti-Myc/FLAG antibodies. Scale bar, 20 μm. F and G, IL-17RD promotes TRAF2 recruitment to TNFR2 in co-IP assays. The relative density of precipitated TRAF2/β-actin was used to present the TNFR2·TRAF2 complex (F). Quantitative results are presented as the mean ± S.D. from three independent repeats of G. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. H, IL-17RD interacts with TRAF2 in HK-2 cells. HK-2 cells treated with or without TNF-α were used to immunoprecipitate complexes after lysis. I–K, TNFR2 facilitates TRAF2 binding to IL-17RD in co-IP assays. The relative density of precipitated IL-17RD/β-actin (J) and TNFR2/β-actin (K), respectively, presented the IL-17RD/TRAF2 and TNFR2·TRAF2 complexes. Quantitative results are presented as the mean ± S.D. from three independent repeats of I. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.