Abstract
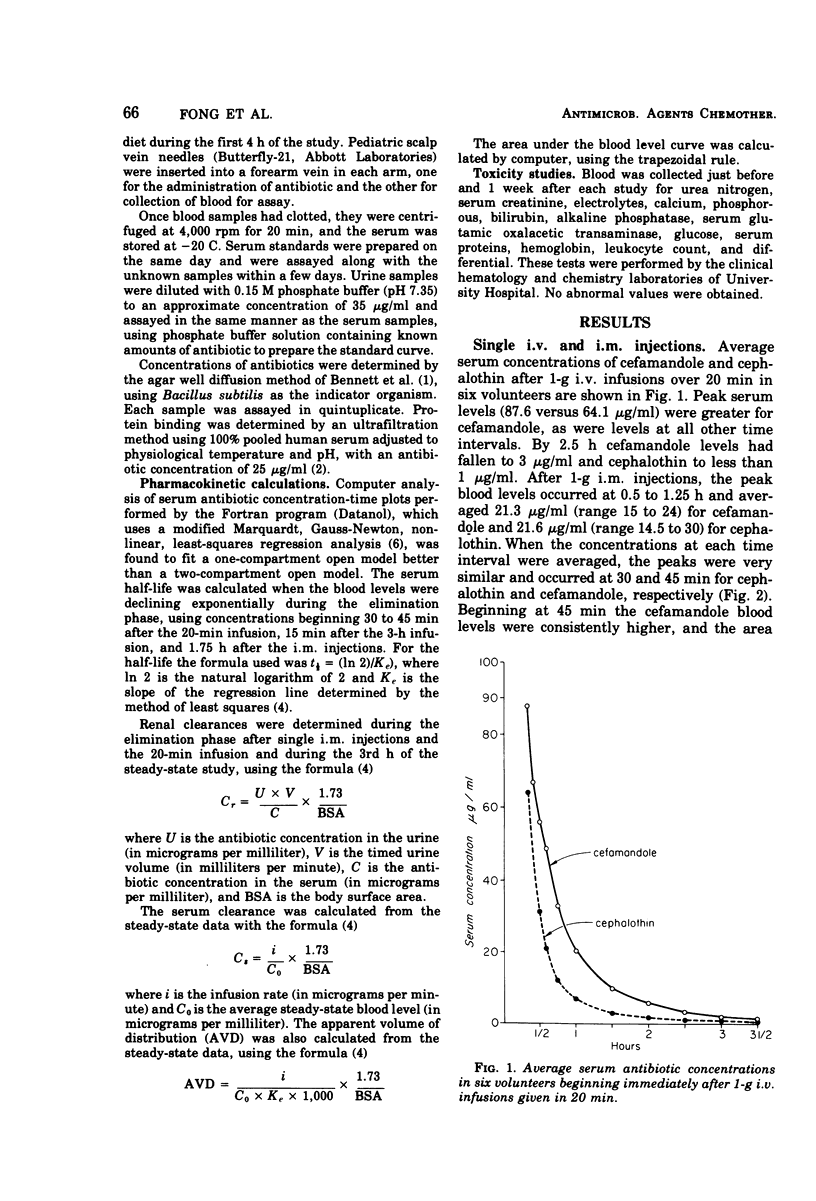
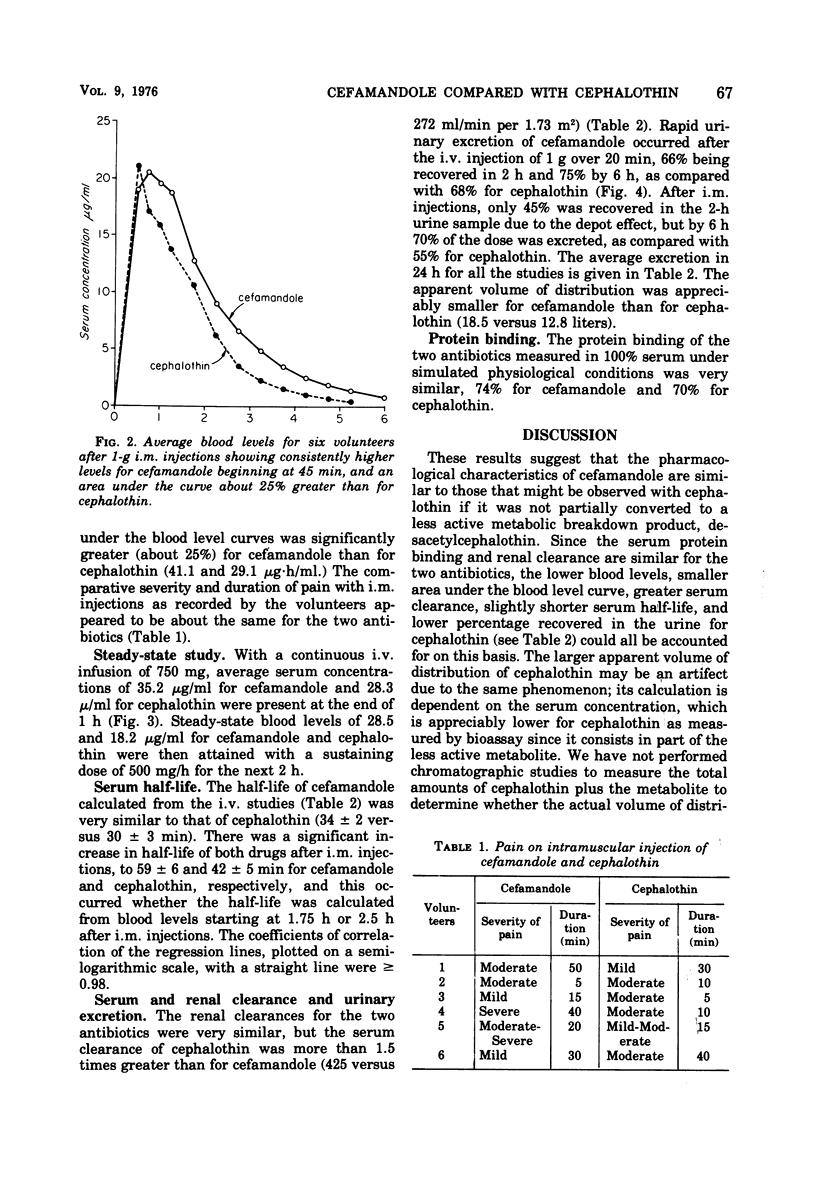
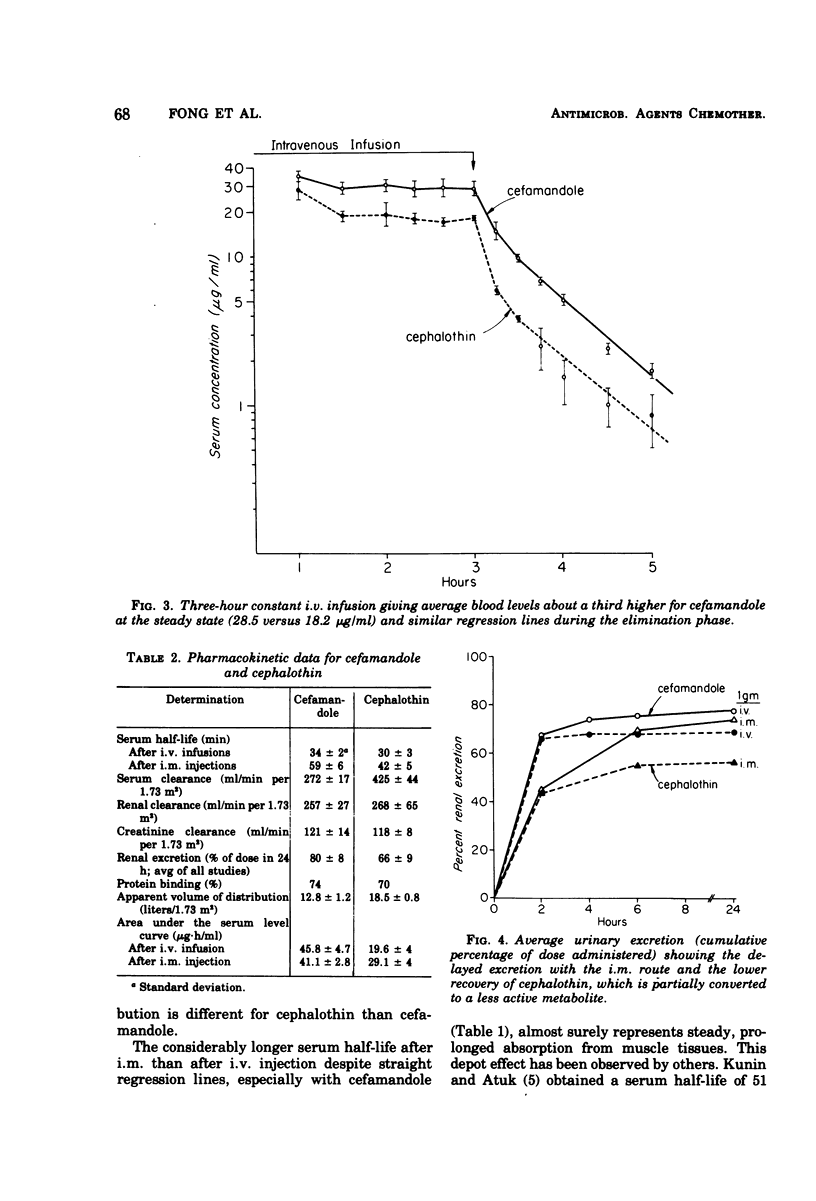
We compared the pharmacology of cefamandole and cephalothin in six healthy adult male volunteers. After a 1-g, 20-min intravenous (i.v.) infusion, the average peak blood level of cefamandole was 87.6 versus 64.1 μg/ml for cephalothin. An i.v. infusion of 500 mg/h for 2 h (after a loading dose of 750 mg) gave an average steady-state blood level of 28.5 μg/ml for cefamandole and 18.2 μg/ml for cephalothin. Mean peak serum levels after 1 g intramuscularly were similar for the two antibiotics (about 21 μg/ml), but with cefamandole they persisted longer, and the area under the blood level curve was about 25% greater. The average t½ as determined from both i.v. studies was 34 min for cefamandole versus 30 min for cephalothin. The mean serum clearance for cephalothin, due to its partial conversion to a metabolite, was much greater than for cefamandole (425 versus 272 ml/min per 1.73 m2), but the renal clearances were similar for the two antibiotics (268 versus 257 ml/min per 1.73 m2). Other values for cefamandole and cephalothin were: 24-h urinary excretion, 80 and 66%; serum protein binding, 74 and 70%; and apparent volume of distribution, 12.8 and 18.5 liters/1.73 m2, respectively. Thus, the pharmacology of the two antibiotics was similar. Blood levels were somewhat higher with cefamandole i.v., but the results suggest that dosage regimens should be the same for the two antibiotics.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett J. V., Brodie J. L., Benner E. J., Kirby W. M. Simplified, accurate method for antibiotic assay of clinical specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):170–177. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.170-177.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. V., Kirby W. M. A rapid, modified ultrafiltration method for determining serum protein binding and its application to new penicillins. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Nov;66(5):721–732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eykyn S., Jenkins C., King A., Phillips I. Antibacterial activity of cefamandole, a new cephalosporin antibiotic, compared with that of cephaloridine, cephalothin, and cephalexin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jun;3(6):657–661. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.6.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M., Atuk N. Excretion of cephaloridine and cephalothin in patients with renal impairment. N Engl J Med. 1966 Mar 24;274(12):654–656. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196603242741205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Cefamandole, a cephalosporin antibiotic with an unusually wide spectrum of activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):177–182. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regamey C., Libke R. D., Clarke J. T., Kirby W. M. Pharmacokinetics of parenteral sodium cephalexin in comparison with cephalothin and cefazolin. Infection. 1974;2(3):132–136. doi: 10.1007/BF01642232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


