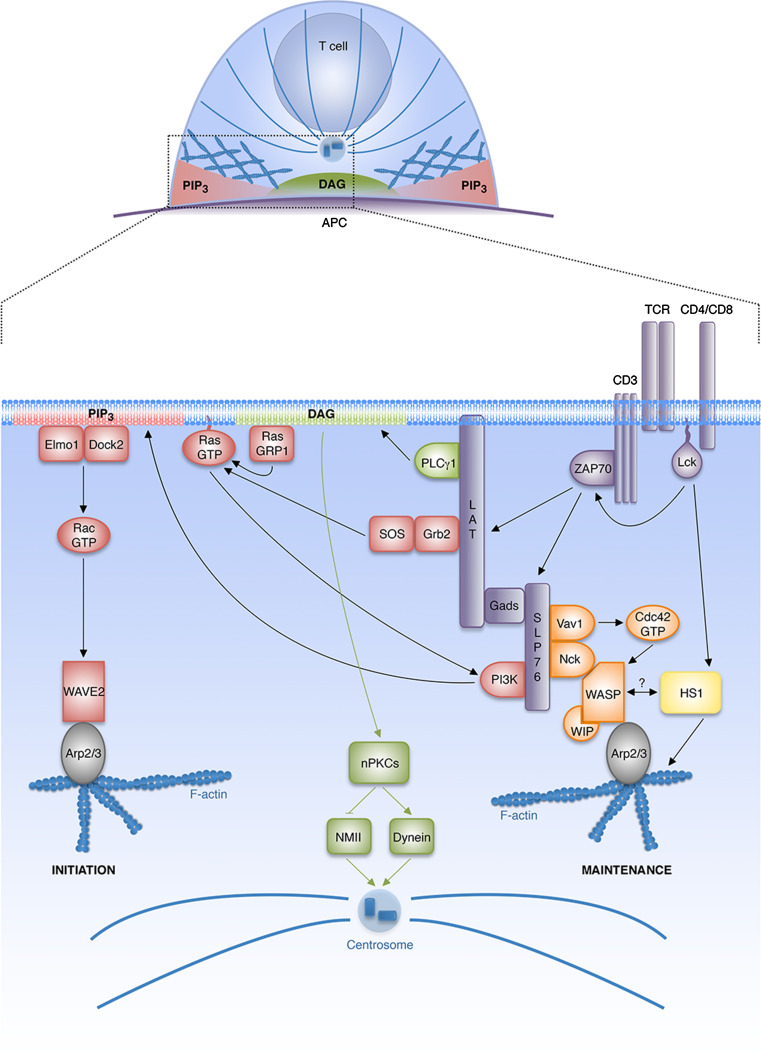
Fig. 2.
Signaling pathways coupling TCR activation to the cytoskeleton. TCR engagement triggers activation of the tyrosine kinases Lck and ZAP-70, which in turn leads to assembly of the LAT-SLP76 signalosome. This complex allows the induction of different signaling pathways leading to the activation of the NPFs WASp, HS1, and WAVE2, which induce local actin polymerization through the Arp2/3 complex. While WAVE2 appears to be critical for the initiation of synaptic actin polymerization, WASp and HS1 might collaborate for the stabilization and the maintenance of the IS. Class IA PI3Ks bind to LAT and SLP76 in a pTyr-dependent manner, and are then activated in a Ras-dependent fashion. SOS, in complex with the adaptor Grb2, and RasGRP1 are two GEFs for Ras that operate downstream of the TCR. PI3K-mediated PIP3 production allows the redistribution of the GEF Dock2 (in complex with Elmo1) to the periphery of the IS, where it drives F-actin remodeling through Rac and WAVE2. Meanwhile, WASp associates with the LAT-SLP76 complex via interaction with Nck and is activated by Cdc42. HS1 is thought to participate in actin dynamics by stabilizing branched-actin filaments generated by Arp2/3 complex activators. TCR engagement also drives centrosome reorientation towards the IS. PLCγ1 is recruited via its interaction with LAT and generates DAG in the synaptic membrane. The DAG gradient induces the recruitment of nPKCs, which mediate centrosome polarization through the regulation of the motor proteins dynein and NMII