Figure 3.
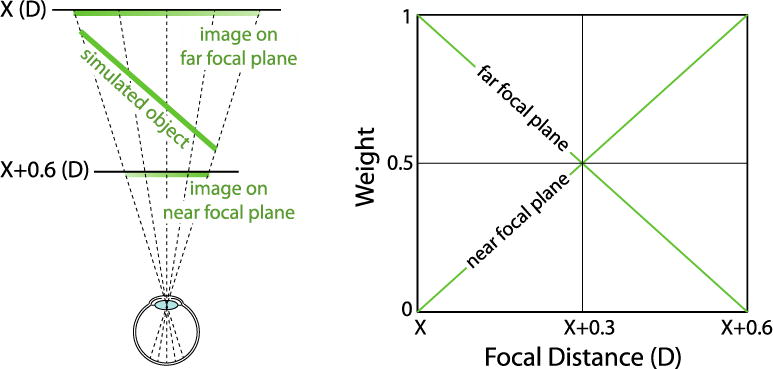
Depth-weighted blending. Left: A slanted plane is simulated between two adjacent focal planes. Pixel intensities are determined on the two focal planes by depth-weighted blending. Each object point on the simulated object is projected onto the two focal planes along a line of sight. The intensity of the image point depends on the dioptric distance from the focal plane to the corresponding object point. Right: The intensity weighting function for the blending. An object at X is on the far plane and hence the full intensity is applied on the far plane. Similarly, an object at X+0.6 has full intensity applied on the near plane. For focal distances between the two planes, the intensity weighting value changes linearly with the change in dioptric distance from the target to each plane.
