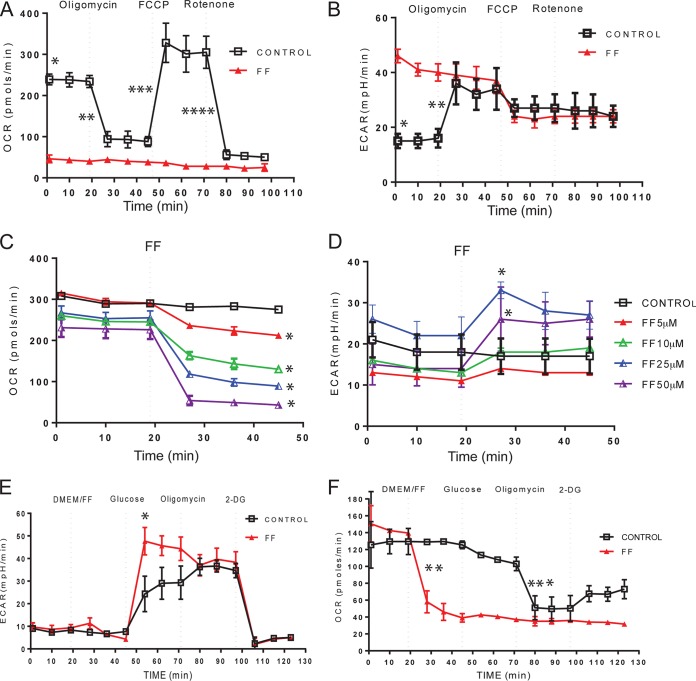
FIG 2.
FF inhibits mitochondrial respiration. Effects of FF on OCR (indicative of respiration) and ECAR (indicative of glycolysis) in human glioblastoma cell line LN-229 determined with an extracellular flux analyzer (XF24; Seahorse Bioscience). (A, B) Cells were plated at 4 × 104/well and cultured in the presence of 10% FBS with or without 50 μM FF for 24 h. Metabolic responses to FF or the vehicle (DMSO) were evaluated after sequential injection of the following metabolic toxins: oligomycin at 0.3 μM, FCCP at 0.5 μM, and rotenone at 0.3 μM. In panel A, a single asterisk indicates a statistically significant difference (homoscedastic Student t test, P ≤ 0.05) between control and FF-treated samples (initial OCR values), two asterisks indicate a significant percent decrease in OCR after oligomycin injection, three asterisks indicate a significant percent increase in OCR after FCCP injection, and four asterisks indicate a significant percent decrease in OCR after rotenone injection. (B) An asterisk indicates a statistically significant difference between control and FF-treated samples (initial ECAR values), and two asterisks indicate a significant percent increase in ECAR after oligomycin injection. (C, D) Immediate OCR and ECAR responses to 0, 5, 10, 25, and 50 μM FF injected at the indicated time points. (E, F) Evaluation of the glycolytic capacity of LN-229 cells. In all of the panels, the data are average values ± the standard deviations from five measurements and each experiment was repeated at least three times (n = 15). In panels C and D, an asterisk indicates a statistically significant difference between control and FF-treated samples calculated for the first time point following FF injection. In panels E and F, an asterisk indicates a statistically significant increase in ECAR between control and FF-treated samples following the addition of glucose, two asterisks indicate a statistically significant decrease in OCR following FF treatment, and three asterisks indicate a statistically significant decrease in OCR between control and FF-treated samples following the injection of oligomycin.