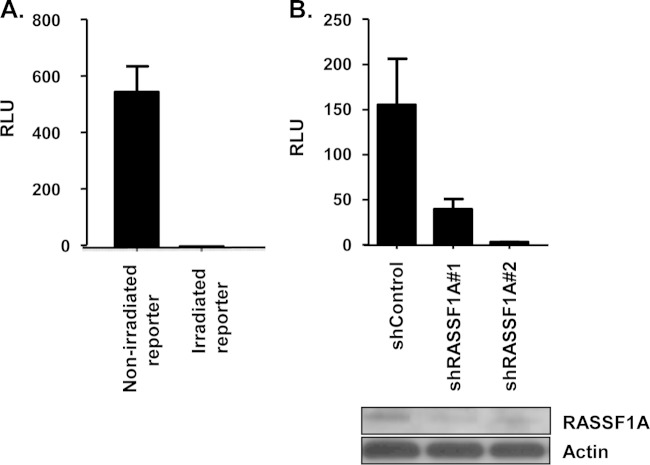
FIG 2.
Suppression of RASSF1A impairs XPA-mediated DNA repair. (A) The CMV-Luc plasmid was irradiated with 900 J/m2 UVC and transfected into XPA-deficient human fibroblasts, and 4 h later, luciferase activity was assayed. The UV-irradiated plasmid showed severely reduced luciferase activity compared to the unirradiated control. (B) XPA-deficient human fibroblasts were stably transfected with 2 independent RASSF1A shRNA constructs and a scrambled control. Cell lines were transiently cotransfected with the irradiated CMV-Luc reporter plasmid together with an expression plasmid for XPA and TK-Renilla as an internal control. DNA repair was assessed by an increase in luciferase activity compared to the renilla luciferase activity (relative luciferase units [RLU]). Data are derived from three independent experiments performed in duplicate, and error bars show standard errors. Data were considered significant at a P of <0.05. Effective knockdown of RASSF1A expression was confirmed by Western blot analysis. Actin was used as a loading control.