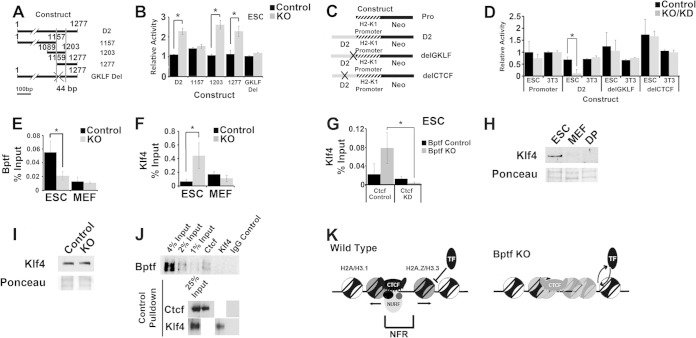
FIG 9.
Bptf regulates Klf4 binding to DNA sequences adjacent to Ctcf with possible consequences for H2-K1 expression. (A) Cartoon of integrating reporter constructs used to identify DNA sequences in D2 (see Fig. 8A and B) with Bptf-dependent regulatory activity using the pNI-MCS integrating reporter vector. The minimal 44-bp fragment required for enhanced Neo reporter expression with Bptf KO is defined with vertical bars. Site-directed mutagenesis was used to delete the GKLF DNA binding site in D2 and is designated by an X. (B) Assay of deletion constructs described for panel A identifies a minimal 44-bp DNA element which is required for enhanced reporter activity with Bptf KO. Site-directed mutagenesis of a GKLF consensus site (delGKLF) in the full-length D2 abolishes enhanced reporter activity with Bptf KO (t test; *, P < 0.05; data are representative of 3 biological replicates). (C) Cartoon of integrating reporter constructs used to assay D2 fragment for Bptf-dependent activity in context with the full-length H2-K1 promoter. Site-directed mutagenesis was used to mutate the GKLF (delGKLF) and Ctcf (delCTCF) DNA consensus sequences in the D2 DNA fragment, as designated by an X. (D) Results from assaying integrating the reporter constructs described for panel C in ESCs and NIH 3T3 fibroblasts. Repression of the H2-K1 promoter by D2 was observed in ESCs with Bptf KO and requires the GKLF and Ctcf binding sites (t test; *, P < 0.05; data are representative of 3 biological replicates). (E) Bptf ChIP at the endogenous D2 site in both control and Bptf KO ESCs and MEFs (t test; *, P < 0.05; data are representative of 3 biological replicates). (F) Klf4 ChIP at the endogenous D2 site in both control and Bptf KO ESCs and MEFs (t test; *, P < 0.05; data are representative of 3 biological replicates). (G) Klf4 ChIP at the endogenous D2 site in both control and Bptf KO ESCs expressing either control of Ctcf KD shRNA expression constructs (t test; *, P < 0.05; data are representative of 3 biological replicates). (H) Western analysis of Klf4 expression in ESCs, MEFs, and DP thymocytes total cell extracts using Ponceau S as a loading control. (I) Western analysis of Klf4 expression in control and Bptf KO from total ESC extracts using Ponceau S as a loading control. (J) Results of a representative in vivo co-IP experiment from total ESC extracts using antibodies to Ctcf and Klf4 or normal IgG. Western analysis for Bptf was performed using an antibody to Bptf. Ctcf and Klf4 IP was controlled by Western blotting using the same antibodies for pulldown. (K) Model for NURF function at Ctcf binding sites. Generalized from our nucleosome occupancy measurements, NURF regulates the NFR at a fraction of Ctcf binding sites. At these sites, NURF could regulate the ability of cell-type-restricted transcription factors (TF) like Klf4 to bind adjacent DNA sequences, with consequences for cell-type-restricted gene expression.